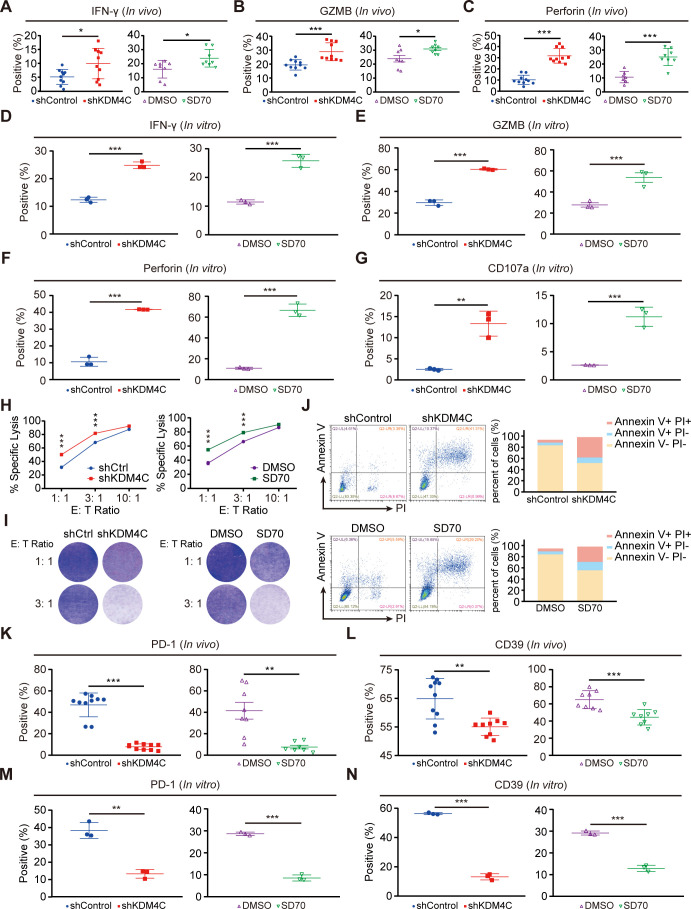
Figure 2.
KDM4C inhibition augments antitumor immunity and delays exhaustion in CD8+ T cells in vitro and in vivo. (A–C) CD8+ T cells isolated from tumor tissues after the indicated treatment were stimulated with PMA (100 ng/mL), monensin sodium salt (1 µg/mL), and ionomycin (100 ng/mL) for 6 hours, and cell cytotoxicity markers (IFN-γ, GZMB and Perforin) were assessed by flow cytometry. *P<0.05, ***p<0.001. (D–G) Evaluation of the effect of KDM4C silencing on the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells in an in vitro conditioned culture model. ***P<0.001. (H) Specific lysis of Lewis tumor cells by CD8+ T cells pretreated with the indicated conditioned medium. Each experiment was repeated three times independently. ***P<0.001. (I) Lewis cells were cocultured with pretreated CD8+ T cells at the indicated proportion for 24 hours, and the T cells were washed and removed with phosphate-buffered saline, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with crystal violet. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. (J) Lewis cells and pretreated CD8+ T cells were cocultured at 1:3. After 24 hours, the tumor cells were stained for an apoptosis assay, and the proportion of apoptotic Lewis cells was detected by flow cytometry. (K, L) After the indicated treatment, the levels of the exhaustion markers PD-1 and CD39 on CD8+ T cells in tumor tissues were assessed. **P<0.01, ***p<0.001. (M, N) Flow cytometry analyses for exhaustion markers on CD8+ T cells treated with the indicated conditioned medium are shown. **P<0.01, ***p<0.001.