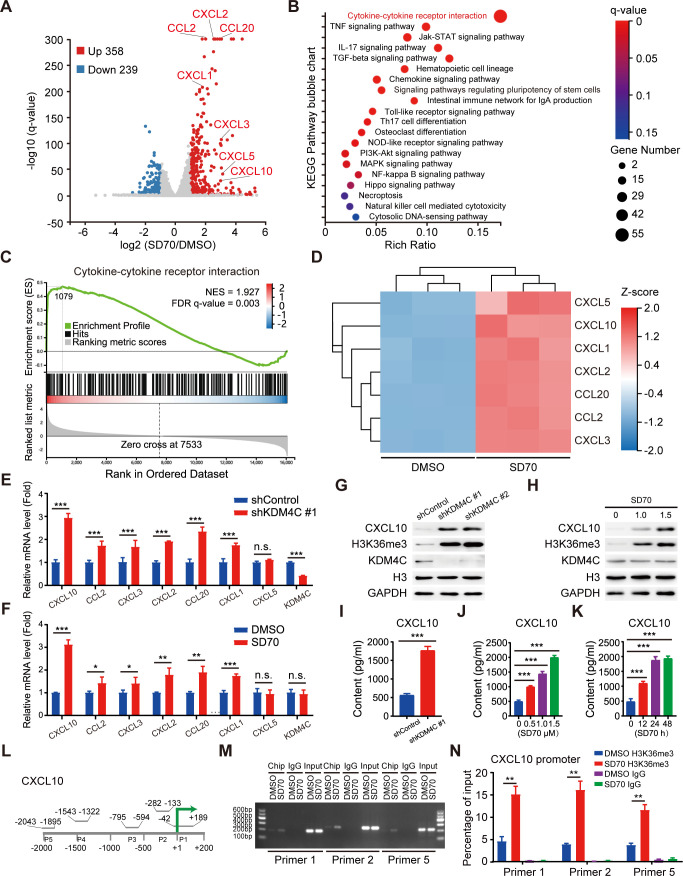
Figure 3.
KDM4C inhibition increases CXCL10 expression by promoting transcriptional activation marker H3K36me3 accumulation at the CXCL10 promoter. (A) The volcano plot shows that differentially expressed genes affected by SD70 were related to the cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction. (B) Bubble chart of signaling pathways affected by SD70. According to classification by KEGG pathway annotations, enrichment analysis was carried out using the phyper function, and the p value was calculated and corrected by the FDR to obtain the q-value function. A q value ≤0.05 was usually regarded as indicating significant enrichment. (C) GSEA of the cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction pathway. (D) Heatmap showing chemokine changes after SD70 treatment. (E, F) The mRNA expression of the indicated genes after the indicated treatment was measured by real-time PCR. Statistical analyses by a t-test. *P<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (n=3). (G, H) Western blotting showing that the protein levels of CXCL10 were increased in KDM4C-silenced Lewis cells (n=3). (I–K) ELISA analysis of CXCL10 expression in shKDM4C Lewis cells compared with control cells (I), cells treated with the indicated concentration of SD70 treatment for 24 hours (J), or cells treated for the indicated time with 1.5 µM SD70 (K). ***P<0.001. (L) Sketch map of the ChIP primer design from −2000 to +200 bp around the transcription start site (TSS). (M) Representative gel electrophoresis result images. The experiment was repeated three times. (N) H3K36me3 levels at the CXCL10 promoter were normalized to the input (mean±SEM; n=3; **p<0.01). ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; NES, normalized enrichment score.