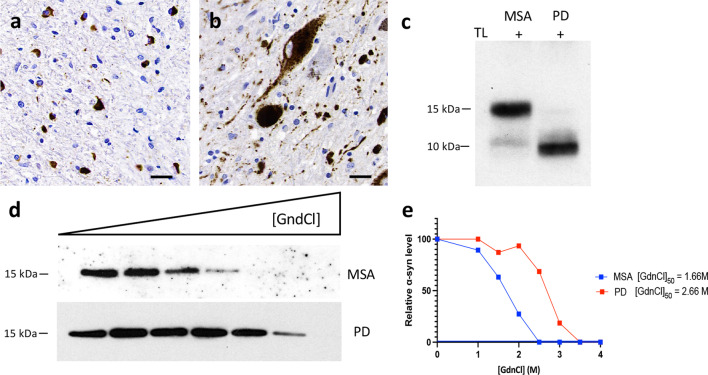
Fig. 2.
Conformational discrimination of α-synuclein strains in PD and MSA brains. a Representative immunohistochemistry image for aggregated α-synuclein in the cerebellum white matter from a MSA patient showing glial cytoplasmic inclusions. b Representative immunohistochemistry image for aggregated α-synuclein in the substantia nigra (SN) from a PD patient showing Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. c Representative total α-synuclein (Syn-1 clone) immunoblots showing the thermolysin (TL) digestion of brain extracts from the cerebellum and the SN of a MSA and a PD patient, respectively. d, e Conformational stability assays for α-synuclein aggregates in brain extracts from patients with MSA or PD. Representative α-synuclein immunoblots (d) and the resultant denaturation curves (e) are shown. The curves depict mean residual α-synuclein values following treatment with the indicated concentrations of GdnCl. Higher GdnCl50 values were obtained for α-synuclein aggregates in the patient with PD than that in the patient with MSA