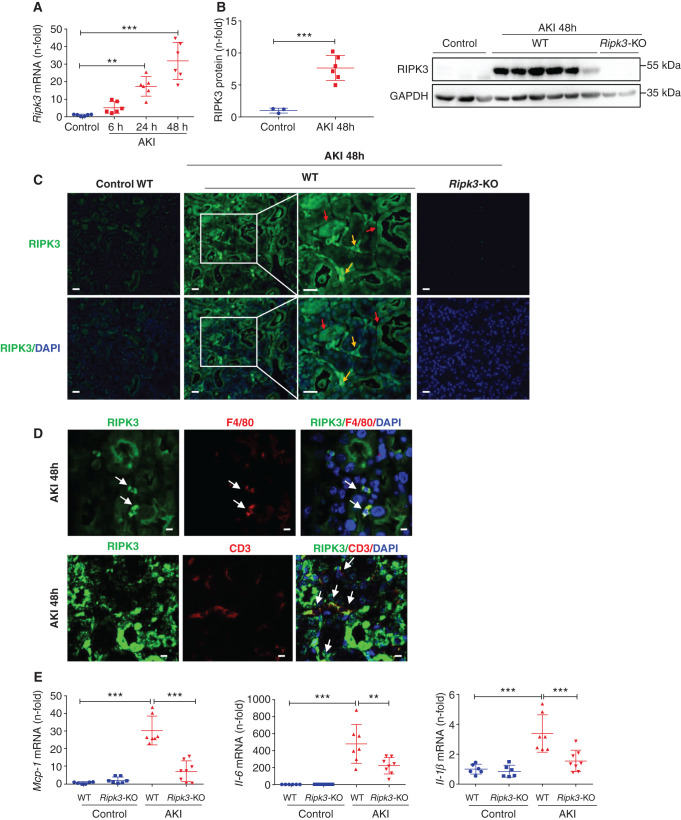
Figure 1.
RIPK3 deficiency prevented the increase in kidney inflammatory mediators in FA-AKI. (A) Time course of kidney RIPK3 mRNA expression in AKI. Mean ± SD of six animals per group. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (B) Quantification and representative western blot of RIPK3 expression in AKI at 48 hours. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Mean ± SD of three to six animals per group. ***P<0.001. (C) RIPK3 immunofluorescence in AKI at 48 hours. Increased RIPK3 expression is observed in both tubules (red arrows) and interstitial infiltrating cells (yellow arrows). Representative images are shown. Magnification, ×200; ×400 in detail. Scale bars, 50 μm. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. (D) Colocalization of RIPK3 with the macrophage marker F4/80 and the lymphocyte marker CD3 in AKI at 48 hours. Confocal microscopy. Magnification, ×800. Scale bars, 5 μm. (E) Kidney Mcp-1, IL-6, and Il-1β mRNA levels are lower in Ripk3-KO than in WT mice in FA-AKI at 48 hours. Mean ± SD of six to eight animals per group. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.