Extended Data Figure 4. Abrogation of SOS induction in the lexA(Ind-) mutant.
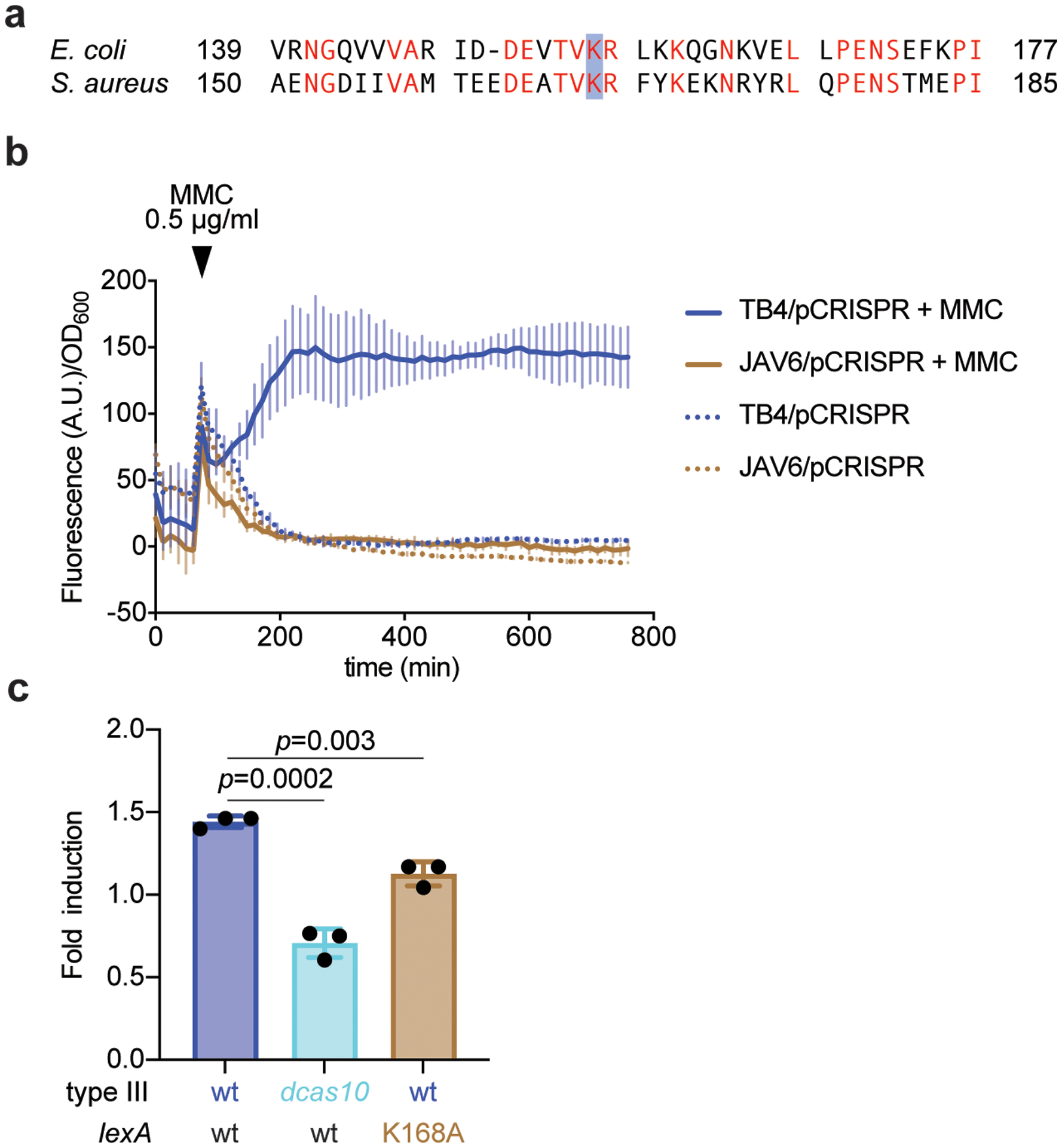
(a) A mutation in lexA that prevents its self-cleavage and the induction of the SOS response, K156A, was previously identified in Escherichia coli. Alignment with the LexA sequence of S. aureus identified K168 as the homologous residue, which was mutated in S. aureus TB4 to alanine to generate strain JAV6. (b) Strains TB4 and JAV6 were transformed with an SOS reporter plasmid, pAV22, carrying the GFP ORF downstream of the promoter for the 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase gene. This promoter is activated after LexA self-cleavage when the SOS response is induced with mitomycin C (MMC). Each strain was either treated or not with MMC and both the growth (OD600) and green fluorescence (arbitrary units, A.U.) were measured over time, to report the fluorescence/growth ratio. (c) qPCR of the SOS-induced polV transcript after infection (with ϕNM1γ6) of cells carrying a wild-type type III-A system in either wild-type or lexA(Ind-) hosts, as well as carrying the dcas10 mutation. RNA was collected when the cultures reached OD600 0.15 (exponential growth phase), after infection at MOI 10, and used for qPCR, using the housekeeping gene rho as an internal reference for each sample. Mean of three independent biological replicates ± s.d. are reported. p-values obtained with two-sided t-test.
