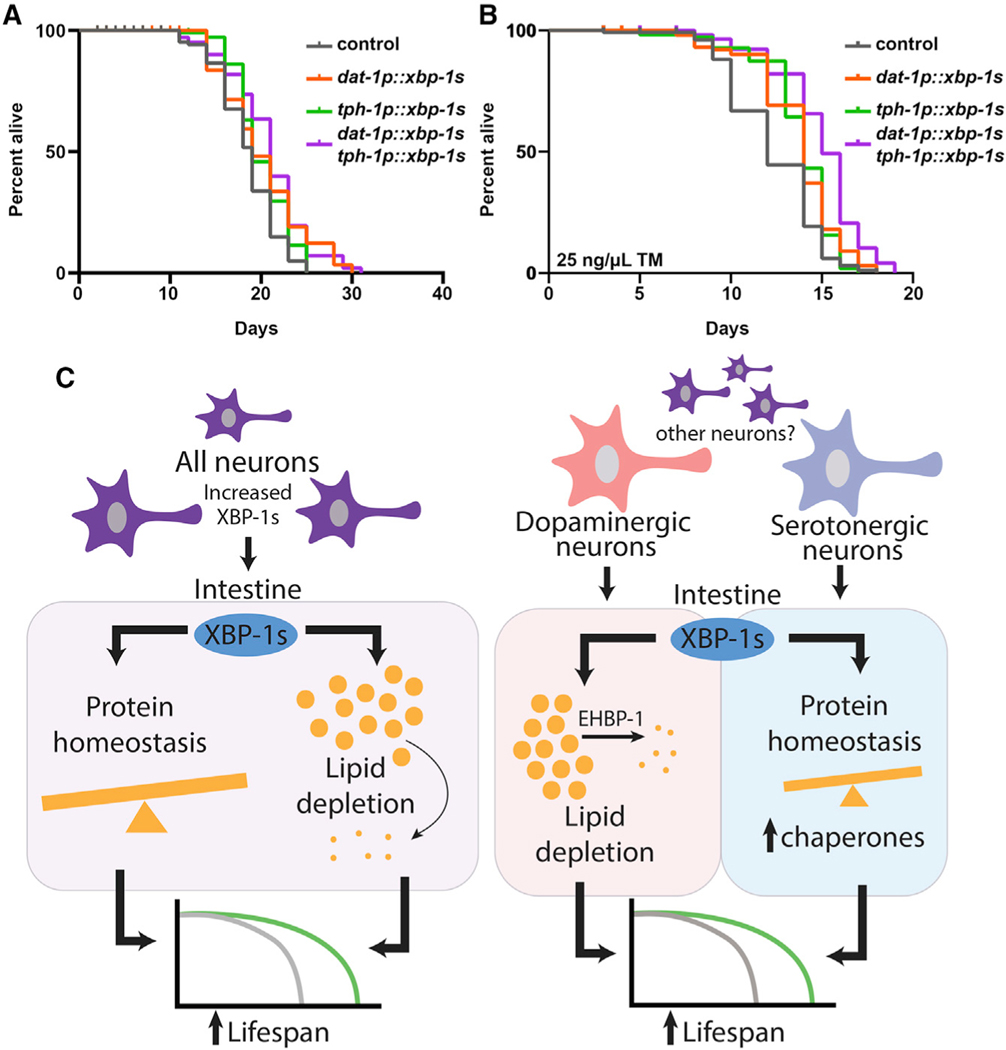
Figure 6. Serotonergic and Dopaminergic Neurons Have Independent Roles in Modulating Unique Branches of Non-autonomous UPRER.
(A) Lifespan measurements of control, serotonergic xbp-1s (tph-1p::xbp-1s), dopaminergic xbp-1 s (dat-1p::xbp-1s), and serotonergic xbp-1 s (tph-1p::xbp-1s)/dopaminergic xbp-1s (dat-1p::xbp-1s) animals. Data are representative of three independent trials. See Table S1–S2 for lifespan statistics.
(B) TM survival assay of control, serotonergic xbp-1s (tph-1p::xbp-1s), dopaminergic xbp-1s (dat-1p::xbp-1s), and serotonergic xbp-1s (tph-1p::xbp-1s)/dopaminergic xbp-1s (dat-1p::xbp-1s) animals. Animals were moved to 25 ng/μL TM plates at day 1 of adulthood. Data are representative of three independent trials. See Table S1–S2 for lifespan statistics.
(C) Schematic/model showing pan-neuronal xbp-1s overexpression results in lifespan extension by two independent mechanisms: activation of chaperones to promote protein homeostasis and activation of an EHBP-1-mediated lipophagy machinery to deplete lipids. Serotonergic xbp-1s is sufficient to drive chaperone induction to ER stress resistance and extend lifespan but fails to activate EHBP-1-mediated lipophagy. In contrast, dopaminergic xbp-1s drives depletion of lipids through EHBP-1 but fails to activate chaperones to promote protein homeostasis. These divergent signals are independent and together impart the beneficial impact of pan-neuronal overexpression of xbp-1s on whole-animal physiology.