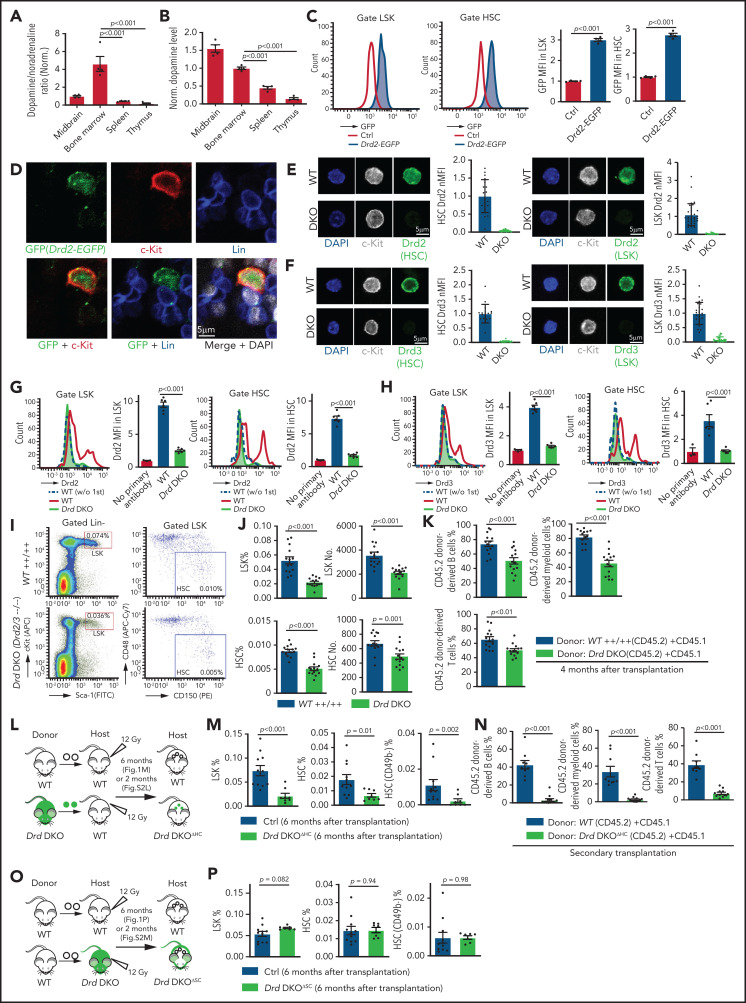
Figure 1.
D2-type dopamine receptors cell-autonomously regulate HSC maintenance. (A) Normalized ratio (normalized to 1) of dopamine/noradrenaline in extracellular fluid from midbrain, BM, spleen, and thymus by ELISA (n = 4 for each tissue). The P values were calculated using analysis of variance (ANOVA). (B) Normalized dopamine level in extracellular fluid of midbrain, BM, spleen, and thymus by ELISA (n = 4). The P values were calculated using ANOVA. (C) Representative FACS graphs and quantification of GFP expression in LSK cells and HSCs from littermate control or Drd2-EGFP transgenic mice (n = 4). The P value was calculated using the Student t test. (D) Representative confocal images showing GFP expression in Lin− c-Kit+ HSPCs in adult bone sections from Drd2-EGFP mice. Confocal images showing Drd2 (E) and Drd3 (F) expression in FACS-sorted HSCs (left panels) and LSK cells (right panels) from WT or Drd-DKO (DKO) mice. Quantification of Drd2 or Drd3 normalized mean fluorescent intensity (nMFI). Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) for WT cells is normalized to 1. For Drd2, WT HSC = 19, DKO HSC = 39, WT LSK = 33, and DKO LSK = 33. For Drd3, WT HSC = 18, DKO HSC = 21, WT LSK = 25, and DKO LSK = 25. Representative FACS graphs showing Drd2 (G) and Drd3 (H) expression in WT and Drd-DKO LSK cells and HSCs. MFI is normalized to the WT sample without primary antibody (n = 3); WT = 6, Drd-DKO = 6. (I) Representative FACS plots of LSK cells and HSCs in Drd-DKO and WT control mice. Numbers in the boxed areas represent the percentage of the corresponding cell population. (J) Quantification of the percentages of LSK cells (upper panels) and HSCs (lower panels) in BM (WT = 14; Drd-DKO = 14). The P value was calculated using the Student t test. (K) Quantification of donor-derived (CD45.2) B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, and myeloid cells in competitive repopulating experiments (WT = 14; Drd-DKO = 14). A total of 5 × 105 CD45.2 (WT or Drd-DKO) BM cells were mixed with 5 × 105 CD45.1 BM cells, transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipients, and analyzed 16 weeks later. The P value was calculated using the Student t test. (L) Diagram depicting transplantation of WT or Drd-DKO LSK cells into lethally irradiated WT mice. (M) Percentages of LSK cells (left panel), HSCs (middle panel), and CD49b− HSCs (right panel) in hematopoietic-specific chimeric WT (n = 11) or Drd-DKOΔHC (n = 8) BM from mice in panel L at 6 months after transplantation. The P value was calculated using the Student t test. (N) Quantification of donor-derived (CD45.2) cells in secondary competitive transplantation experiments (WT donor BM = 9; Drd-DKOΔHC donor BM = 12). The P value was calculated using the Student t test. (O) Schematic diagram depicting transplantation of WT LSK cells into lethally irradiated WT or Drd-DKO recipients. (P) Percentages of LSK cells (left panel), HSCs (middle panel), and CD49b− HSCs (right panel) from chimeric mice in panel O at 6 months after transplantation. The P value was calculated using the Student t test. WT = 11; Drd-DKOΔSC = 7. APC, allophycocyanin; Ctrl, control; Fig.S2L, supplemental Figure 2L; Fig.S2M, supplemental Figure 2M; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PE, phycoerythrin.