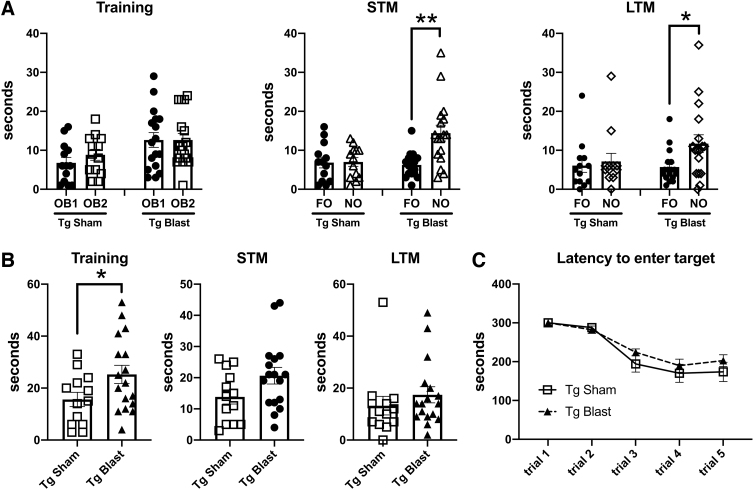
FIG. 8.
Novel object recognition (NOR) and Barnes maze testing of cohort 2. Blast-exposed (n = 16) and sham-exposed (n = 16) amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 (APP/PS1) transgenic (Tg) mice from cohort 2 were tested in a NOR and Barnes maze. Panel (A) shows time spent exploring the objects (OB1 and OB2) during the NOR training session as well as exploration of the previously presented familiar object (FO) compared with the novel object (NO) when presented 1 h (short-term memory, STM) or 24 h (long-term memory, LTM) later. Panels (B) shows the total time spend exploring the objects during the indicated NOR sessions. Panel (C) shows the latency to enter the escape hole in the Barnes maze. A repeated measures analysis of variance revealed a significant within subjects effect by trial (F 2.731, 76.456 = 48.668, p < 0.001) but no effect of trial*condition (F 2.731, 76.456 = 1.054, p = 0.370) or between subjects effects (F 1, 28 = 0.971, p = 0.333). Error bars in all panels indicate the standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate values significantly different (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, unpaired t tests).