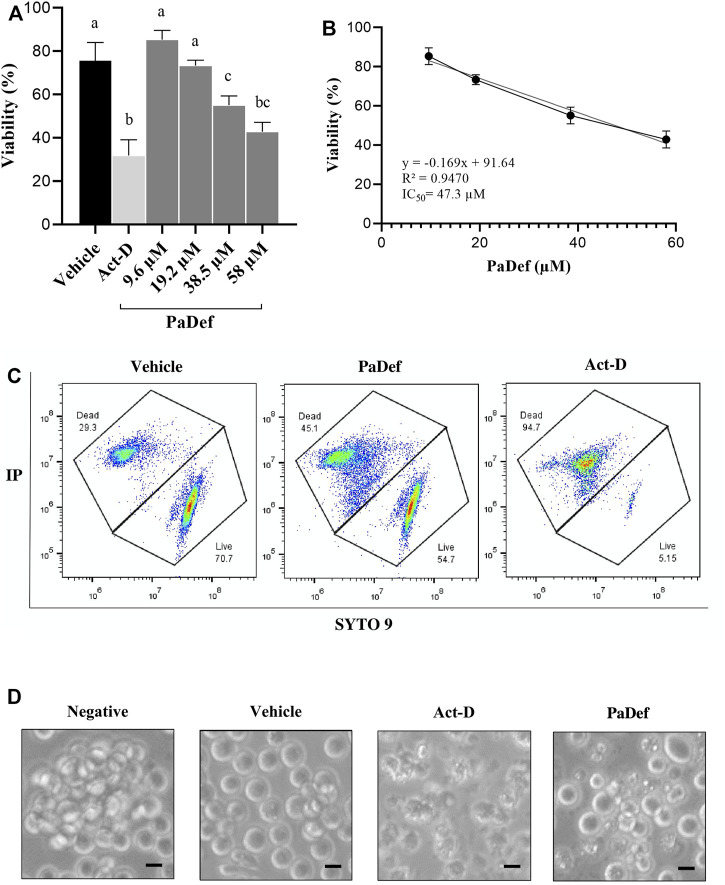
FIGURE 1.
The antimicrobial peptide PaDef is cytotoxic to Jurkat acute lymphoid leukemia cells. (A) Effect of PaDef on the viability of Jurkat cells. Cells were treated under increasing concentrations of the peptide (9.6, 19.2, 38.5, and 58 μM) for 24 h and analyzed by MTT. The data show the percentage of cell viability. DMSO (0.98%) was used as a vehicle and Actinomycin D 0.5 μM (Act-D) as a positive death control. Data represent the mean of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Different letters denote significant differences within the treatments (one-way ANOVA and Tukey´s comparison, p ≤ 0.05). (B) The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated by linear regression analysis; IC50: 47.3 μM; R2 = 0.9470. (C) Evaluation of PaDef IC50 by flow cytometry. Representative plots of the different treatment conditions are shown. Cells were treated with PaDef and vehicle (DMSO 0.98%), Actinomycin D 0.5 µM (Act-D) was used as a positive death control, and 10,000 events were analyzed. (D) Cell morphology of Jurkat after 24 h of treatment. Representative photographs taken by light-field microscopy are shown. Vehicle (DMSO 0.98%), PaDef 47.3 μM and Actinomycin D (Act-D) 0.5 μM. Scale bar 20 μm.