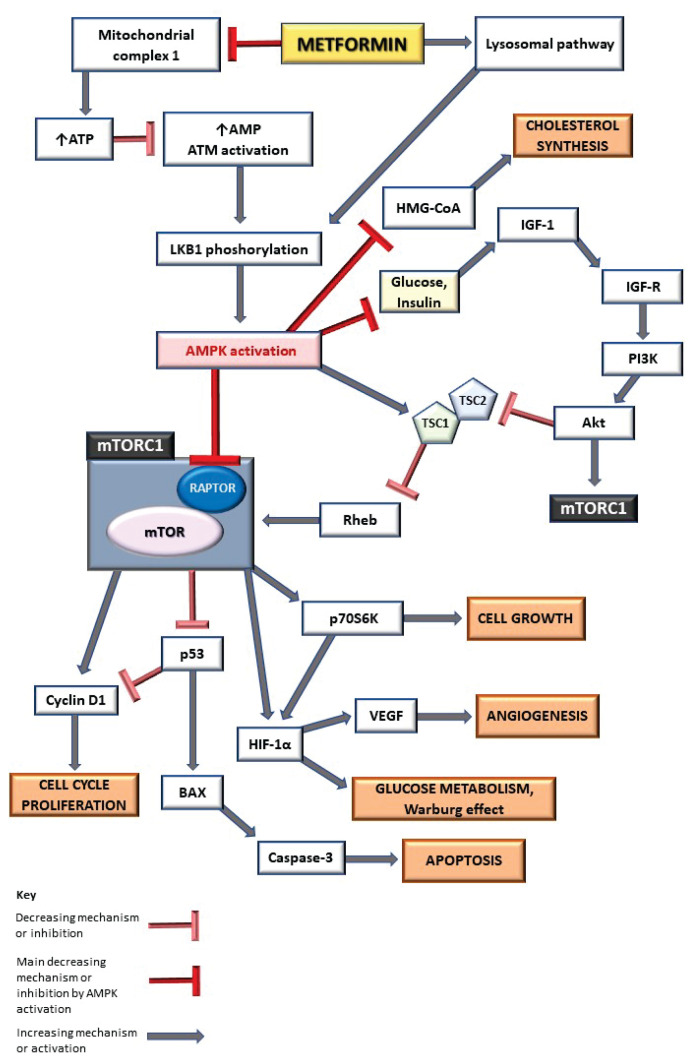
Fig. 2.
The role of MTF in metabolism and cancer process through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. AMPK activation inhibits mTORC1, leading to decreasing of cell growth, angiogenesis and Warburg effect, and increasing of apoptosis. ATP adenosine-triphosphate, AMP adenosine-monophosphate, ATM ataxia telangiectasia mutated, LKB1 liver kinase B1, AMPK adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase, HMG-CoA β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A, IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor 1, IGF-R insulin-like growth factor receptor, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, Akt protein kinase B, mTORC1 mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1, TSC1,2 tuberous sclerosis complex 1,2, Rheb Ras homolog enriched in brain, RAPTOR regulatory-associated protein of mTOR, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, p53 tumor suppressor protein, p70S6K p70S6 kinase, HIF-1α hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, BAX BCL-2 associated X protein.