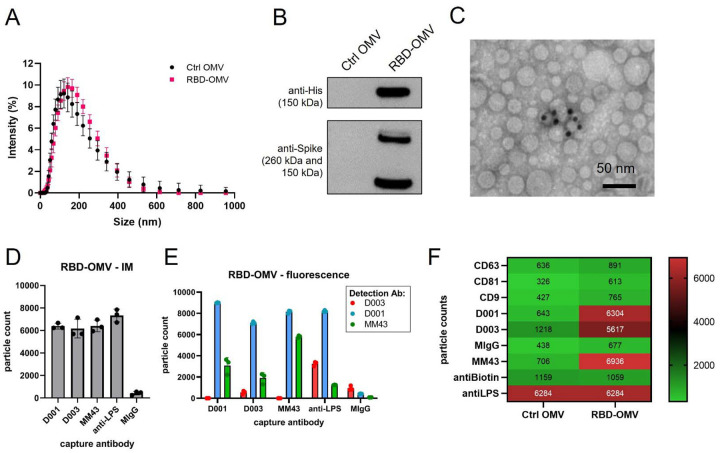
Figure 3.
RBD-OMV characterization. A) Particle concentration and size were determined by DLS. Ctrl-OMVs and RBD-OMVs had comparable particle size distribution, with a mean diameter of 118 nm for Ctrl OMV and 125.6 nm for RBD-OMVs. B) Western blot of Ctrl-OMVs and RBD-OMVs probed with anti-His and anti-Spike antibodies. C) Immunogold transmission electron micrograph with anti-Spike-MM43 and streptavidin-gold (10 nm). D) SP-IRIS of RBD-OMVs captured by antibodies against Spike (D001, D003, MM43), anti-LPS, and mouse-IgG isotype control (MIgG). Interferometric imaging (IM) results are light grey bars. Data points show particle counts per capture spot, n=3 capture spots. E) Labeling with fluorescently labeled antibodies D001, D003, and MM43 shows localization of CoV2-Spike epitopes on RBD-OMVs (colored bars). Data points show particle counts per capture spot, n=3 capture spots. F) Heatmap of SP-IRIS data comparing RBD-OMVs from (D) and Ctrl-OMVs. Particle counts for each marker were normalized by LPS content (see also Supplementary Figure S2).