Figure 6.
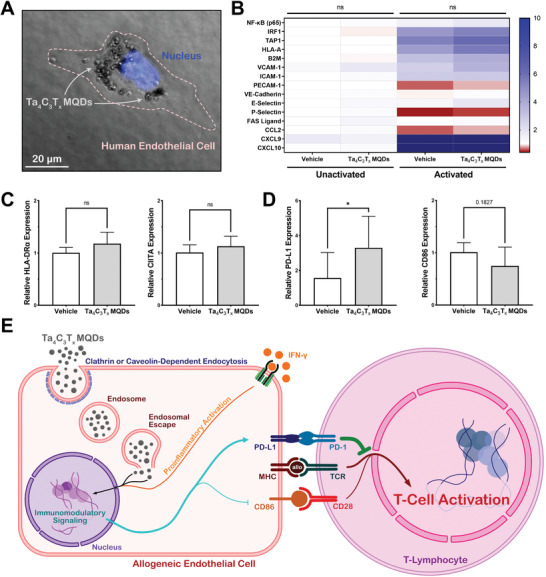
Mechanistic evaluation of the immunomodulatory effects of Ta4C3T x MQDs. A) Light microscopy demonstrated that Ta4C3T x MQDs were readily internalized into HUVECs after 24 h of culture. B,C) Quantitative PCR analysis was used against genes involved in antigen presentation, cellular adhesion, lymphocyte recruitment, and chemokine signaling. Activation of HUVECs using IFN‐γ resulted in an increase in proinflammatory signaling. No significant differences were observed between cells treated with 20 µg mL−1 of Ta4C3T x MQDs and the vehicle control. D) Treatment with Ta4C3T x MQDs was found to alter the expression of the T‐cell co‐inhibitor PD‐L1 and the T‐cell coactivator CD86 on the surface of activated HUVECs. A significant increase was noted in the endothelial expression of PD‐L1, and a trend toward a decrease of CD86 was observed after treatment with 20 µg mL−1 of Ta4C3T x MQDs. E) Schematic representation of the immunomodulatory mechanisms of Ta4C3T x MQDs. MQDs are internalized into cells through active endocytosis, after which their surface architecture facilitates endosomal escape. They then participate in immunomodulatory signaling to alter the ratio of surface coactivator and co‐inhibitors, which subsequently results in reduced T‐cell activation.
