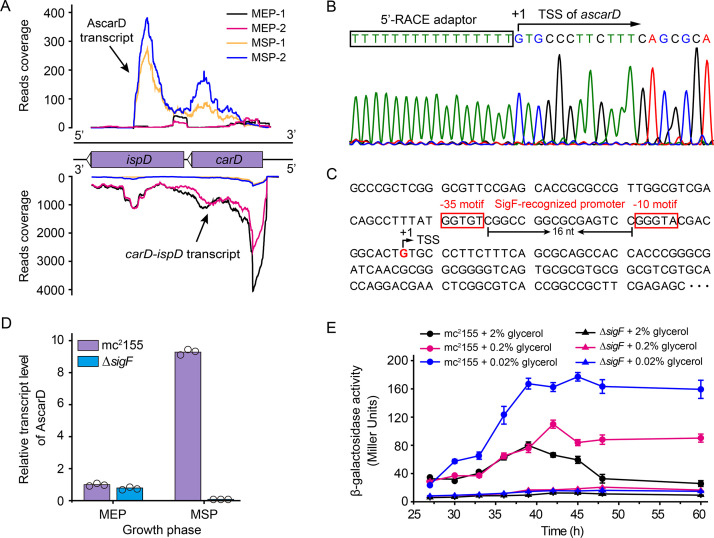
Figure 4. Identification and characterization of AscarD.
(A) Transcriptional landscapes of carD-ispD transcript and AscarD. Red and black lines represent exponential-phase cells, blue and green lines are from stationary-phase cells. Extensions of −1 and −2 represent two biological replicates. (B) Mapping of the transcriptional start site (TSS) of AscarD. The lower four-color chromatogram shows the results of Sanger sequencing, and the corresponding DNA sequence is displayed on the upper layer. The 5′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′-RACE) adaptor sequence is framed by a black rectangle, and TSS is indicated by a black arrow. (C) Potential SigF-recognized −10 and −35 motifs upstream of the identified TSS are indicated with red rectangles. (D) AscarD transcript levels at different growth phases of mc2155 and ΔsigF strains were measured by qRT-PCR, normalized to sigA transcript levels, and expressed as fold change compared to levels of mc2155 cells at mid-exponential phase (MEP). Individual data for the three biological replicates are shown in the corresponding columns. (E) Promoter activities of ascarD in mc2155 and ΔsigF strains carrying a β-galactosidase-encoding reporter plasmid. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of three biological replicates.