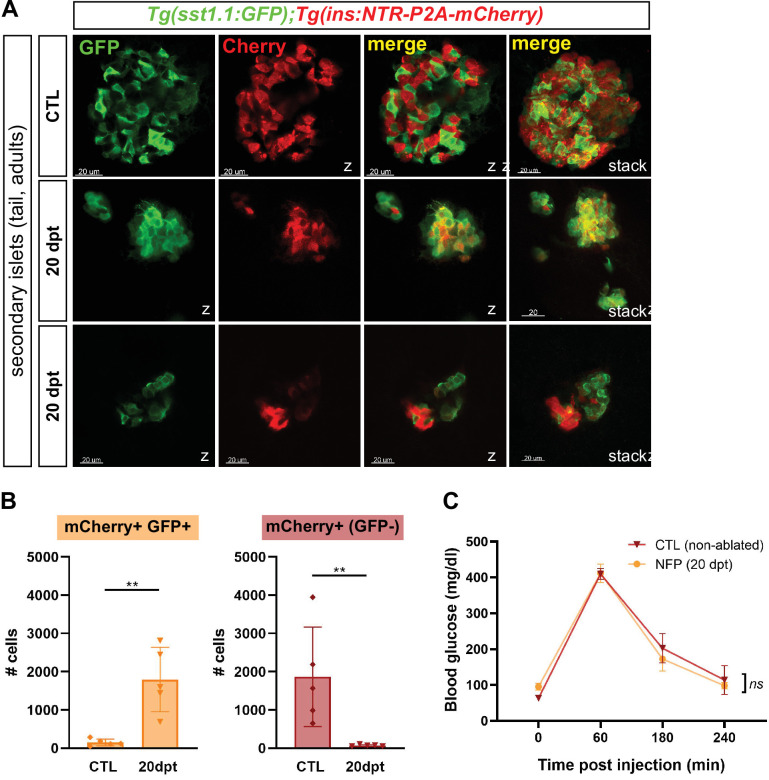
Figure 4. Bihormonal cells are the main source of Insulin in the whole pancreas after regeneration and regulate blood glucose homeostasis.
(A) Whole mount immunofluorescence (GFP and mCherry) on the pancreas of Tg(sst1.1:eGFP); Tg(ins:NTR-P2A-mCherry) adult zebrafish showing secondary islets in the pancreatic tail. One representative CTL and two independent 20 dpt samples are shown. Coexpressing cells appear in yellow due to overlapping GFP and mCherry staining. Confocal optical section (Z-planes) and 3D projections (stacks) are shown. (B) Quantification of monohormonal mCherry+ β-cells and GFP+ mCherry + bihormonal cells detected by FACS in the tail of CTL fish and after 20 days regeneration (20 dpt). Mann-Whitney test. p** = 0.0079 in both graphs. Mean ± SD. (See also Figure 4—source data 1). (C) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test performed in adult zebrafish. Blood glucose was measured over time in control (non-ablated, DMSO) and NFP-treated (ablated) fish after intraperitoneal injection of 0.5 mg/µl of D-Glucose. 4≤ N ≤ 9 per time point for CTL and NFP. Two-way ANOVA test with Sidak’s multiple comparison test. Mean ± SEM; ns: not significant.