Figure 2: Increased arginine-stimulated insulin secretion after insulin pre-exposure in healthy humans.
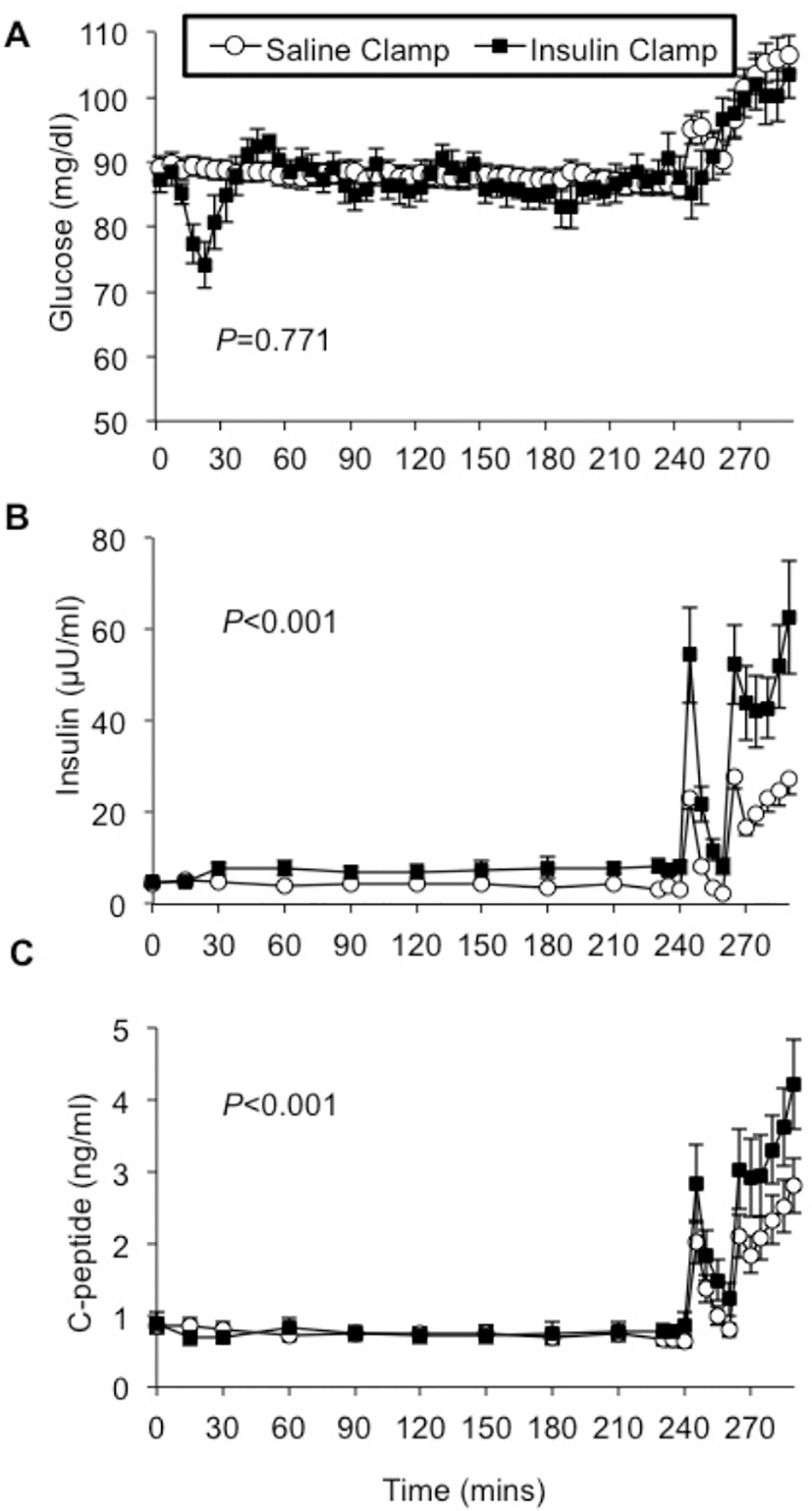
Each participant underwent two study visits during which either a 4-hour sham/saline infusion or a hyperinsulinemic clamp was performed, and then arginine was administered to stimulate endogenous insulin secretion as both a 5g intravenous bolus (at time 240 minutes), and a 500 mg/kg continuous infusion (time 260–290 minutes). Plasma glucose levels were overall well matched throughout both studies after stabilization and before arginine [A]. Arginine bolus and infusion increased endogenous insulin [B] and C-peptide [C] concentrations, and these responses were significantly augmented after insulin pre-exposure. Saline clamp (○), insulin clamp (●).
