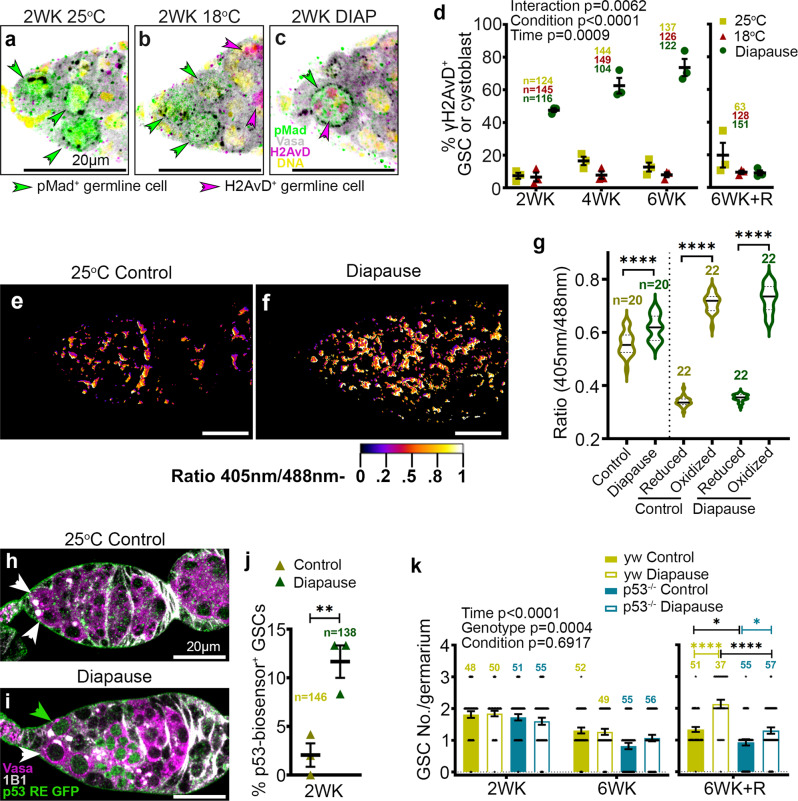
Fig. 4. DNA damage, ROS, and p53 mediated protective response in diapause.
a–c Confocal micrographs of germaria from flies maintained for 2 weeks (WK) at 25 °C (a), 18°C (b), or diapause conditions (c). Anti-pMad (green) labels cells with active Dpp signaling from the niche. Anti-γH2AvD (magenta) labels cells with double-strand DNA breaks due to damage [magenta arrowheads in (c)] or meiosis (arrowheads in (b)). d Percentage of H2AvD+ cells out of total pMad+ cells from 25 °C, 18 °C, and diapause over time. R, recovery. Statistical analysis is by 2-way ANOVA before recovery and 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test after recovery. e, f Ratiometric (405 nm/488 nm) confocal micrographs of germaria from tubulin-mito-roGFP2-Orp1 flies kept for 2 weeks at 25 °C [control (e)] and in diapause (f). g Quantification of ROS in the germarium relative to maximally reduced (with dithiothreitol) or oxidized (with diamide, see methods for details). Statistical analysis is by 1-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ****p < 0.0001. h, i Confocal micrographs of germaria from flies maintained for 2 weeks (WK) at 25 °C (h), or diapause conditions (i). Anti-Vasa labels germline cells (magenta) and 1B1 stains the Hts protein indicating spectrosome/fusome (GSCs are shown by arrowheads). p53 RE GFP-NLS biosensor (green) labels cells with p53 activity (green arrowhead in (i)). j Percentage of p53 RE GFP+ GSCs out of total GSCs from 25 °C control and diapause for 2WK. p value from unpaired two-tailed t-test. **p = 0.0095. k Quantification of GSC number/germarium from y, w control flies and p53−/− in 25 °C control and diapause from 2WK, 6WK, and 6WK recovery (6WK + R). Statistical analysis is by three-way ANOVA before the recovery and one-way ANOVA after recovery. n is the number of GSCs analyzed in (j), in all other cases, n = number of germaria analyzed. Data are mean ± s.e.m. *p = 0.0211; *p = 0.0346; ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars are 20 µm.