Figure 1:
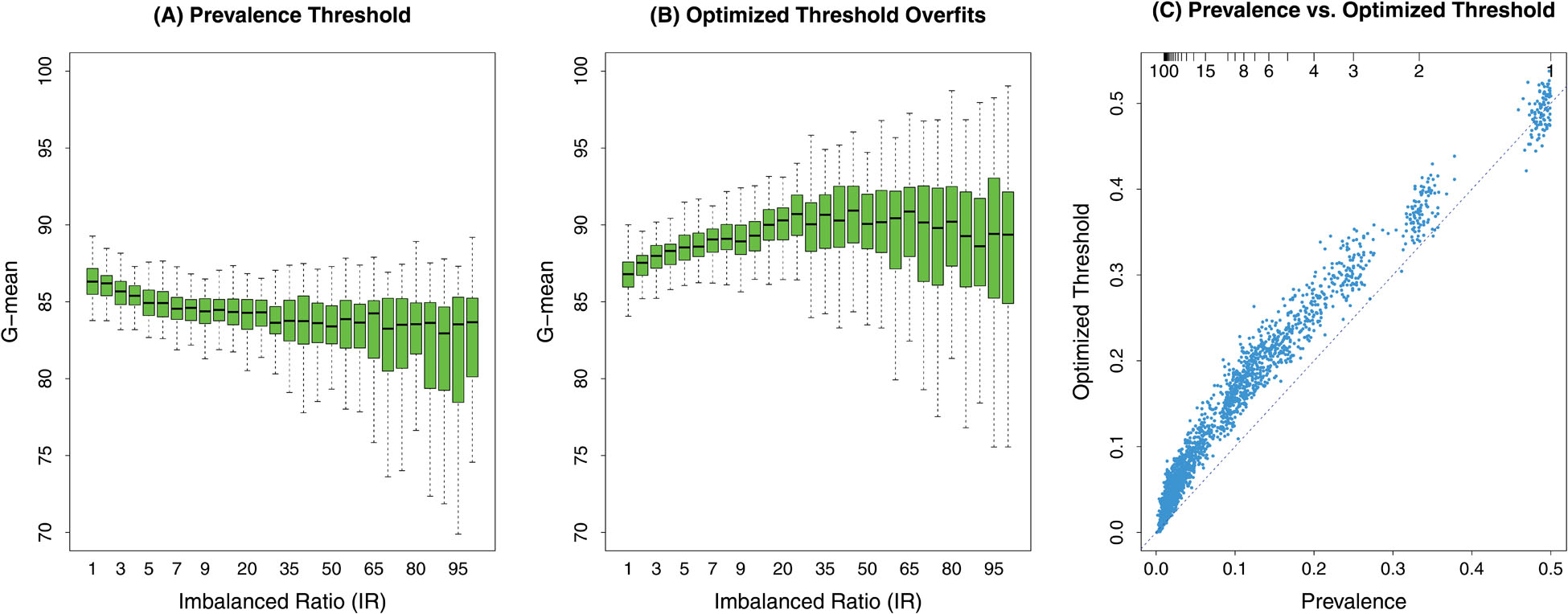
G-mean (Geometric mean) soft classification performance of the ML method random forest (RF). Data is classified as a rare case if RF out-of-bag (cross-validated) probability is larger than a specific threshold value. Classification data were simulated 100 times independently under Imbalanced Ratio (IR) varying from balanced (IR=1) to extreme imbalanced (IR=100) scenarios. (A) Threshold for RF classification equals prevalence (fraction of rare cases), a method called RFQ [6]. Performance of RFQ is excellent across all IR values. (B) Threshold for RF classification is selected by maximizing out-of-bag (cross-validated) G-mean. Even though optimization uses cross-validated values, results are optimistically biased as evident by G-mean values increasing with IR. (C) Optimized threshold values are inflated when compared to prevalence threshold values (the only exception being IR=1 when data is balanced; top right). Combined, this demonstrates optimality of RFQ (q*-classification) while avoiding double dipping the data.
