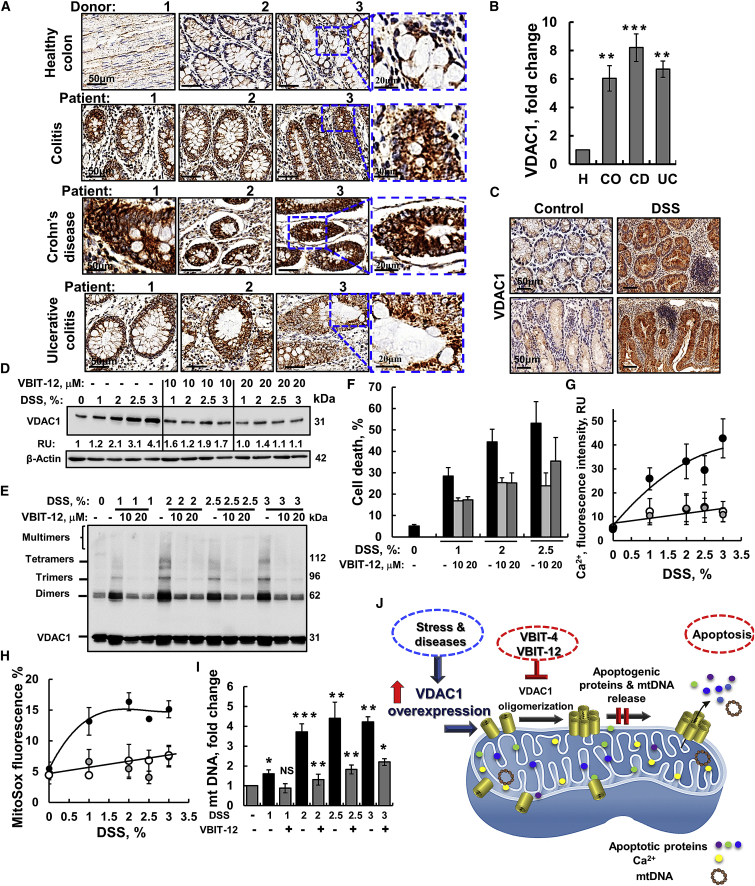
Figure 1.
VDAC1 is overexpressed in human colon pathologies and in DSS-treated cells, which result in VDAC1 oligomerization, apoptosis, and mtDNA release that are inhibited by VBIT-12
Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of VDAC1 was performed on tissue microarray slides obtained from Biomax US (Cat No. CO245). The array contains colon sections from healthy (H, 4 samples), colitis (Co, 4 samples), ulcerative colitis (UC, 4 samples), and Crohn’s disease of the ileocecal junction (CD, 4 samples). (A) Representative sections of the indicated tissues were IHC stained for VDAC1 using specific antibodies. Scale bars are 20 or 50 μm, as indicated. (B) Quantitation of VDAC1 expression levels in the whole area of the provided sections. Staining intensity was quantified using a panoramic microscope and HistoQuant software. Results, mean ± SEM, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, NS not significant (n = 4 for each group). (C–E) Representative images of colon tissue sections from control and DSS-induced colitis mice, IHC, stained for VDAC1 (C; n = 6 for control and n = 7 for DSS). Scale bar is 50 μm. (D–I) CT-26 cells were incubated with the indicated DSS concentration for 48 h in the presence or absence of VBIT-12 (10 or 20 μM) (n = 3). Then samples were analyzed for VDAC1 expression level by immunoblotting with acting serving as loading control (D), oligomerization (E), apoptosis (assayed by PI staining and flow cytometry) (F), intracellular Ca2+ levels (G), mtROS (H), and mtDNA release (I); all were assayed as described in the Materials and methods section. Results, mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, n = 3, NS, not significant. (J) Proposed coupling of VDAC1 overexpression induced by pathological conditions (IBD) and VDAC1 oligomerization mediating the release of apoptogenic proteins from the IMS, leading to apoptosis and the release of mtDNA, leading to inflammasome activation. These processes are inhibited by the VDAC1-interacting molecules, VBIT-4 and VBIT-12, via preventing VDAC1 oligomerization.