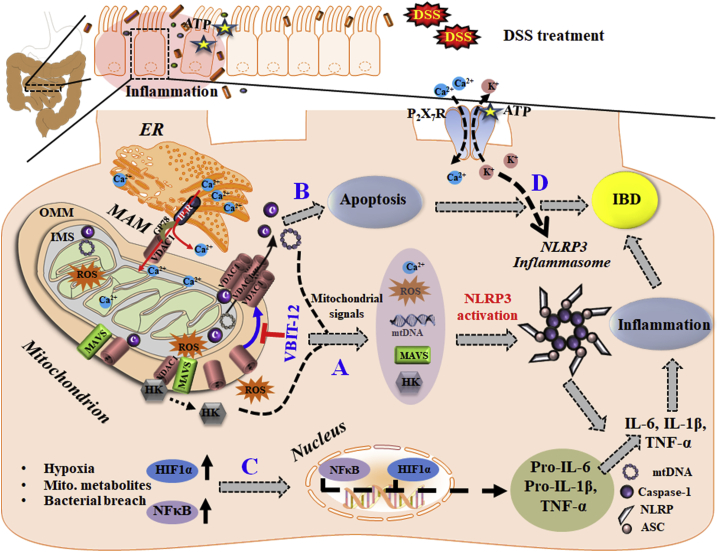
Figure 8.
Schematic model of the function of mitochondria, VDAC1, and associated proteins in the apoptosis, inflammasome activation, and inflammatory response leading to IBD, and their prevention by VBIT-12
VDAC-1 is involved in numerous mitochondria-associated functions including epithelial metabolism, inflammation, and apoptosis, all impaired in IBD. VDAC1 overexpression induced by stress conditions (DSS) triggers mitochondria dysfunction and four major signaling pathways: (A) Mitochondrial signals (mtDNA release, increased mtROS and Ca2+ levels, HK detachment, and MAVS assembly) that induce NLRP3 assembly and activation, leading to pro-inflammatory activation and IBD development. MAVS, which interacts with VDAC1, stabilizes the inflammasome complex and activates NLRP3 on the MAMs. In addition, intracellular Ca2+ signaling is controlled by the MAM tether comprising VDAC1, IP3R, and other proteins. These signaling molecules facilitate the inflammasome assembly and activation, leading to pro-caspase-1 activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine maturation. (B) The apoptosis pathway is induced by oligomerization of the overexpressed VDAC1 to form a large channel-mediating cyto c release, apoptosome formation, caspase activation, and apoptotic cell death. The same oligomeric VDAC1 channel allows the release of mtDNA. (C) The HIF-α/NF-κB/MIF-regulated gene expression pathway may be induced by mtROS/hypoxia. The activation of HIF1-α and of NF-κB by the bacterial flora of the gut increases the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines. (D) NLRP3 activation is triggered by various stress signals including the activation of P2X7R by ATP release from cells, leading to K+ efflux and influx of Ca2+, both of which contribute to the activation of NLRP3, which activates caspase-1 and initiates an intestinal inflammatory cascade. In this model, the overexpression and oligomerization of VDAC1 acts as a common functional junction for all these activated pathways in IBD. Hence, inhibition of VDAC1 oligomerization by VBIT-12 suppresses apoptosis and inflammation to prevent the IBD pathology.