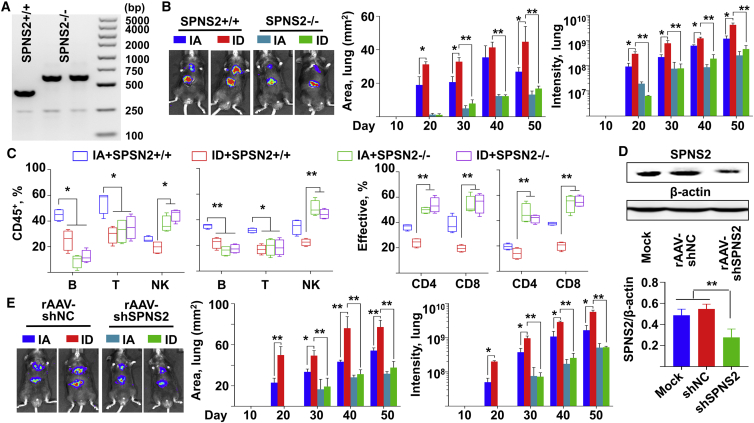
Figure 6.
Inhibition of SPNS2 reduced the effect of ID on HCC pulmonary metastasis in vivo
(A) Genome typing of the WT (SPNS2+/+, 409bp) and SPNS2-knockout (SPNS2−/−, 613 bp) mice. (B and C) WT and SPNS2-KO mice were fed with either IA or ID diet at day −7. Mouse HCC H22 cells were orthotopically administrated at day 0. All mice were sacrificed at day 50. n = 4. (B) Growth of tumor cells over time in the lung of WT and SPNS2-KO mice. Representative figures were taken at day 50. (C) The percentage of lymphocyte subsets and that of effective T cells in the liver (left) and lung (right) were determined by flow cytometry assay. Effective: CD 44high, CD62Low. (D) The SPNS2 expression in the liver of C57BL/6 mice at 1 month-post rAAV vector administration. Both representative figures and quantitative data of western blot assay were shown. n = 3. (E) Growth of orthotopically injected mouse HCC H22 cells over time in the lung of C57BL/6 mice, following rAAV8 vector administration. See protocols for in vivo imaging in Figure S5A. Representative figures were taken at day 50. n = 3. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.