Figure 5.
IFNα-induced CD169+ macrophages enhanced phagocytotic and autologous T cell-activating abilities in vitro
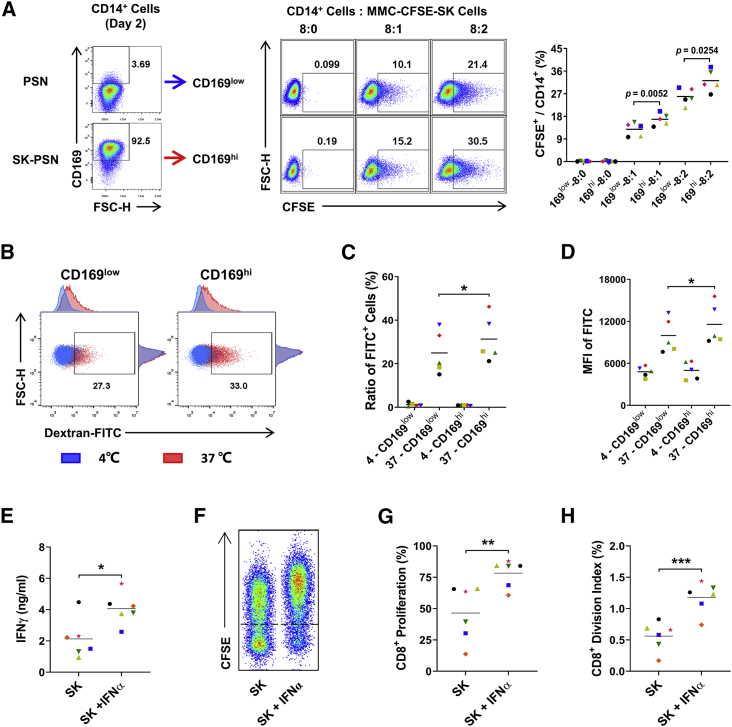
(A–D) CD14+ monocytes were precultured with PSN or SK-PSN in the presence of SK TCS for 2 days, and CD169low or CD169hi monocytes were collected for further phagocytosis assays. (A) Monocytes (5 × 105 cells) were cocultured with mitomycin C-treated and CFSE-labeled SK tumor cells in the indicated ratios for 20 h. Phagocytosis was measured by flow cytometry, and the percentage of CFSE+ monocytes is shown; n = 5. (B–D) Monocytes (5 × 105 cells) were incubated with 1 mg/mL dextran-FITC molecules for 60 min at 0°C (to measure non-specific adherence) or at 37°C (to measure phagocytosis), and the ratio of FITC+ cells and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of FITC on CD14+ cells were measured by flow cytometry; n = 5. (E–H) CD14+ monocytes were incubated with or without 10 pg/mL IFNα2 in the presence of SK TCS. Two days later, pretreated monocytes were cocultured with CFSE-labeled autologous CD3+ T cells for 5 days (monocyte/T cell ratio of 1:2); n = 6. (E) IFNγ in the supernatant was detected by ELISA. (F–H) CD8+ T cell proliferation was detected by flow cytometry. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; paired Student’s t test (A, C–E, G, and H).