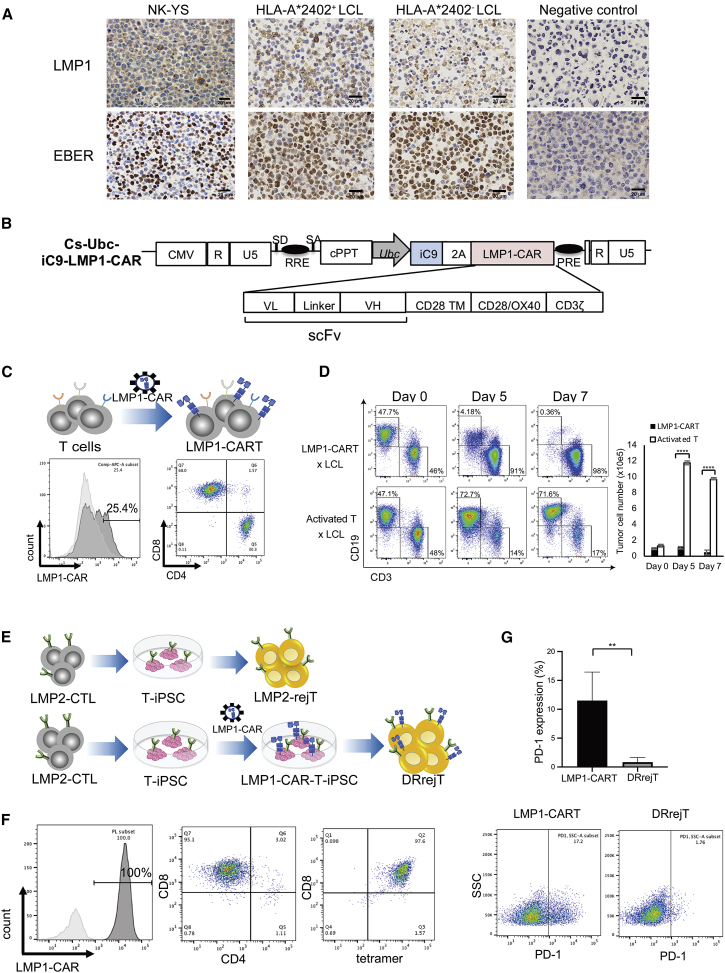
Figure 1.
Generation and validation of LMP1-CARTs
(A) LMP1 expression and EBV-encoded small RNA (EBER) in situ hybridization of EBV+ cell lines and EBV− cell line as negative control. Scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Schematic of the lentiviral iC9-CAR vector containing Ubc promoter. CAR contains an scFv derived from heavy (VH) and light chain (VL) variable regions of an anti-LMP1 antibody. TM, transmembrane (CD28). The vector contains the suicide gene iC9, cleavable 2A-like sequence. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of expression of LMP1-CARs in PMBC-derived LMP1-CARTs detected by protein L, which binds to the scFv of CAR, followed by streptavidin-APC staining and determination of APC signal. The data represent at least five independent experiments using four different donors. (D) PBMC-derived LMP1-CARTs and lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) were cocultured (ratio 1:1). Cultures were collected, stained with anti-CD3 and anti-CD19 antibodies, and analyzed by flow cytometry on days 0, 5, and 7. The plots represent three independent experiments. Cells were counted using counting beads on flow cytometry. Graph summarizes the results of total cell number of LCLs. Error bars represent ± SEM. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. (E) Schematic illustrations of generation of LMP2-rejTs and DRrejTs. T-iPSCs established from LMP2-specific CTL clones were differentiated into LMP2-rejTs. T-iPSCs established from LMP2-specific CTL clones were transduced with lentiviral LMP1-CAR vector and LMP1-CAR-T-iPSCs were differentiated into DRrejTs. (F) Flow cytometric analysis of LMP1-CAR transgene expression (left), CD4 and CD8 expression (center), and LMP2 antigen specificity detected by PE-conjugated HLA-A∗2402/LMP2131–139 tetramer (right) in DRrejTs. (G) Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) expression in LMP1-CARTs and DRrejTs detected by flow cytometry. Error bars represent ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01 by unpaired Student’s t test. The plots represent four independent experiments.