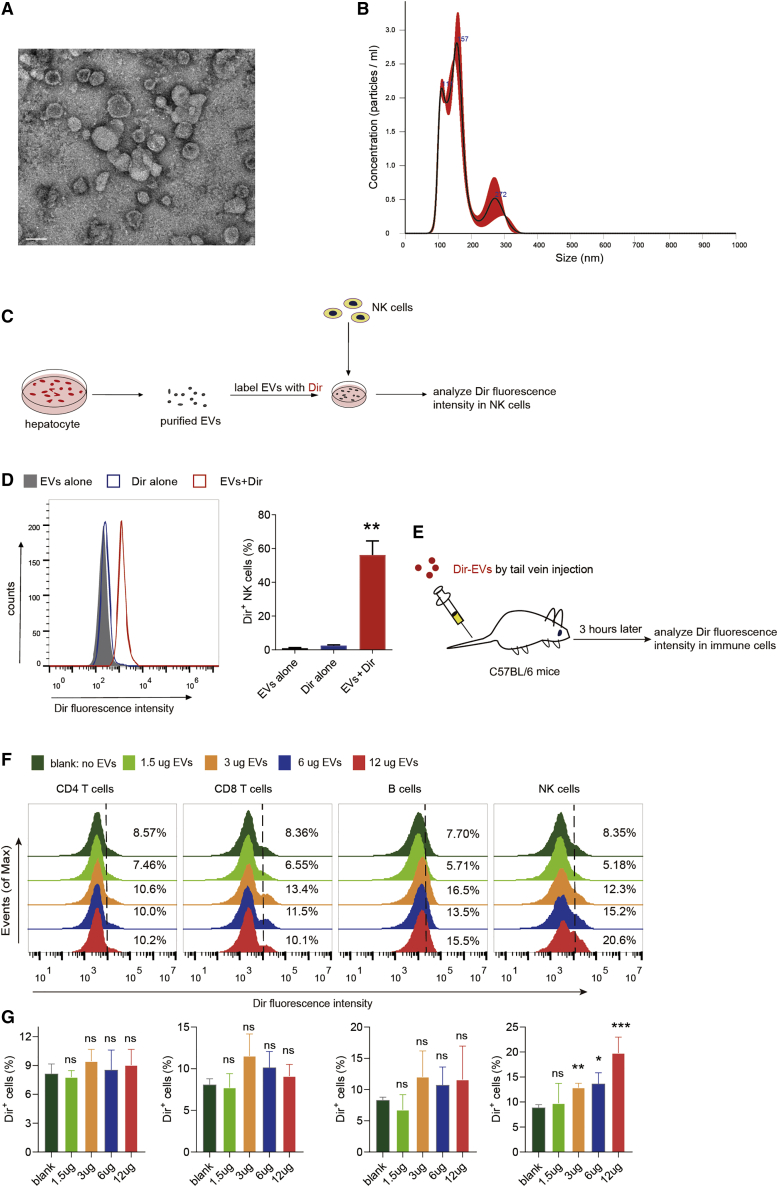
Figure 3.
NK cells act as major immune cell recipients of hepatocyte-derived EVs
(A) Representative image of HHL5 cell-derived EVs by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Scale bar, 100 nm. (B) Size distribution of HHL5 cell-derived EVs using nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). (C) Experimental scheme illustrating EV uptake process by NK cells. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of NK cells incubated with Dir-labeled or -unlabeled, HHL5 cell-derived EVs. Dir-alone samples represent mock EV preps generated from Dir-labeled, EV-free medium. (E) Experimental scheme of EV uptake assays in various immune cell populations (NK, T, and B cells, for instance) in liver. (F and G) Representative histograms (F) and quantifications (G) of Dir fluorescence intensities in hepatic CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, B cells, and NK cells using different concentrations of EVs. See also Figure S4.