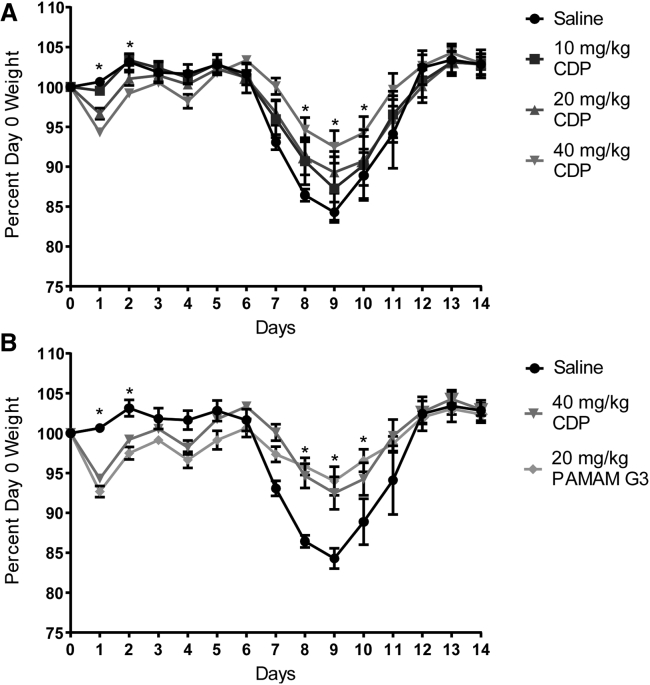
Figure 4.
Treatment with CDP is beneficial for maintaining weight and recovery of PR8-infected mice
(A) Mice treated with 10, 20, or 40 mg/kg CDP compared with weights of the saline control group, represented as a percentage of their day 0 weight. (B) Mice treated with 20 mg/kg PAMAM G3 compared with the 40 mg/kg CDP and saline control groups from above. A comparison of mice treated with 40 mg/kg CDP and 20 mg/kg PAMAM shows comparable maintenance of weight throughout the study. A two-way mixed ANOVA was run to determine the effect of PAMAM G3 and doses of CDP versus saline over time on weight following influenza infection over time. Data in graphs are mean ± standard error of the mean; n = 8. There was a statistically significant interaction between treatment and time on weight; F (56, 450) = 3.189, p < 0.0001. Post hoc analysis via Tukey’s multiple comparisons test revealed that CDP treated mice at 40 mg/kg were significantly heavier than saline-treated mice on day 8 (mean difference (diff), 1.66 g; p = 0.046), day 9 (mean diff, 1.86 g; p = 0.021), and day 10 (mean diff, 1.84 g; p = 0.048) after infection. Similarly, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test revealed that PAMAM G3-treated mice at 20 mg/kg were significantly heavier than saline-treated mice on day 9 (mean diff, 2.18 g; p = 0.010) and day 10 (mean diff, 2.24 g; p = 0.034) after infection. An asterisk represents significant difference between one or more of the treatment groups compared with saline treatment.