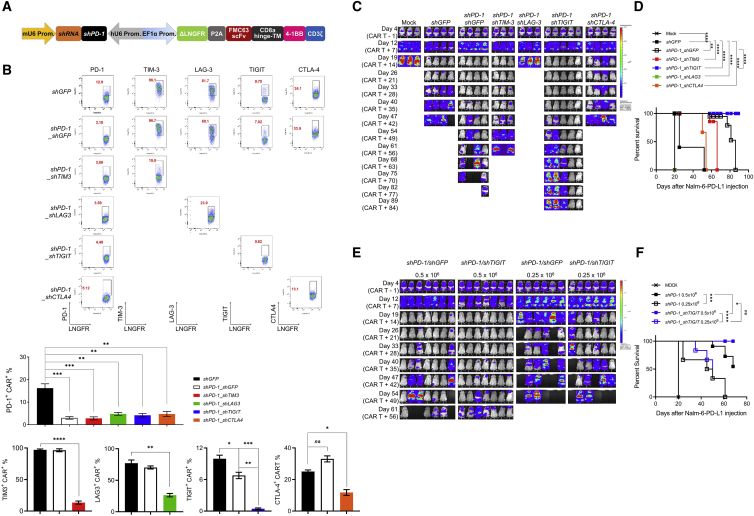
Figure 3.
Simultaneous downregulation of PD-1 and TIGIT further enhances the in vivo functionality of CD19-targeting CAR T cells
(A) Schematic representation of the engineered two-in-one vector system carrying dual shRNA cassettes for two ICRs. (B) Dual downregulation efficiency of each ICR in CAR T cells stimulated for 48 h with gamma-irradiated K562-CD19 cells. FACS plots are representative data from two independent experiments performed in duplicates, and the bar graphs are the pooled mean ± SD. (C) NSG mice were injected intravenously with 1 × 106 Nalm-6-GL-PD-L1 leukemia cells. 5 days later, 1 × 106 CAR T cells with each dual downregulation (shGFP, shPD-1/shGFP, shPD-1/shTIM-3, shPD-1/shLAG-3, shPD-1/shTIGIT, shPD-1/shCTLA-4) were injected intravenously. Tumor burden was monitored based on the bioluminescence intensity from the IVIS imaging system. Data are from n = 3 mock, shPD-1/shTIM-3, and shPD-1/shLAG-3, n = 4 shGFP, shPD-1/shGFP, and shPD-1/shCTLA-4, and n = 5 shPD-1/shTIGIT. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test comparing each CAR T treated mice from (C). (E) NSG mice were injected intravenously with 1 × 106 Nalm-6-GL-PD-L1 leukemia cells. 5 days later, 0.5 × 106 or 0.25 × 106 CAR T cells with PD-1 (shPD-1/shGFP) or PD-1/TIGIT (shPD-1/shTIGIT) downregulation were injected intravenously. Tumor burden was monitored based on the bioluminescence intensity from the IVIS imaging system. Data are from n = 7 mice for the 0.5 × 106 dose groups and n = 6 mice for the 0.25 × 106 dose groups. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test comparing CAR T treated mice from (E). Statistical analysis for (B) was done by one-way ANOVA. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.