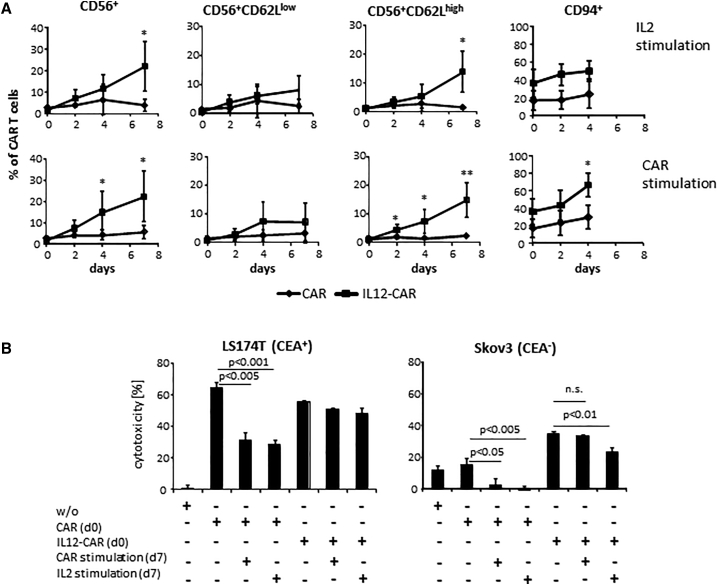
Figure 6.
CAR stimulation induced NK-like differentiation and conserved CAR-specific cytotoxicity of IL12-CAR T cells
(A) T cells were engineered with the IL12-CAR and conventional CAR, respectively, both with the same specificity for CEA. After engraftment (day 0) cells were further stimulated in presence of IL2 (50 U/mL) or the CAR-specific anti-idiotypic antibody BW2064 (2 μg/mL) as surrogate antigen. Cells were analyzed for the indicated markers by flow cytometry. Numbers represent mean values of three to five different donors ±SD. Significant differences were calculated by Student's t test. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗p < 0.05. (B) CAR T cells were tested for CAR-specific and NK-like cytotoxicity before (day 0) and after CAR-specific stimulation through an anti-idiotypic antibody at day 2 and day 4. CAR T cells were co-cultivated (2 × 104 cells/well) at day 0 or day 7 with CEA+ LS174T or CEA− Skov3 tumor cells (each 2 × 104 cells/well) for 48 h. To remove remaining CAR-specific anti-idiotypic antibody from day 7 cultures, CAR T cells were washed extensively before co-cultivation with target cells. Viability of tumor cells was determined by the XTT assay and specific cytotoxicity was calculated. Numbers represent mean values of technical replicates ±SD. Representative data of two independent experiments are shown. Statistical differences were calculated using Student's t test. n.s., not significant.