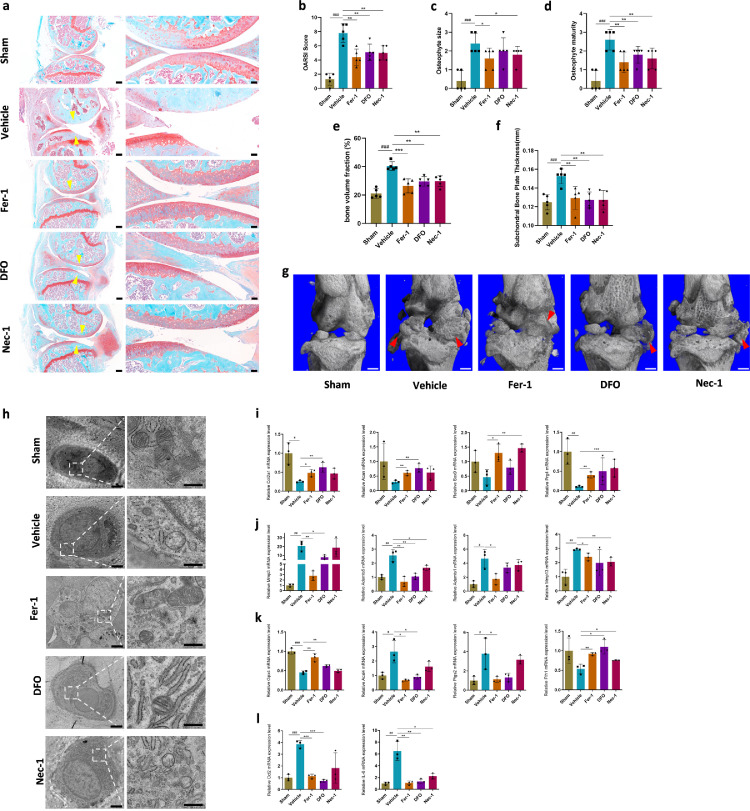
Figure 3.
Fer-1 and DFO attenuated osteoarthritis (OA) development through inhibiting chondrocytes ferroptosis. (a) Representative safranin O-fast green images of osteoarthritic knee joints, that were collected 8 weeks after ACLT surgery. Yellow arrowheads indicate articular cartilage degradation. n = 5; Scale bar, left, 200 μm; right, 50 μm. (b) The severity of OA-like phenotype was analyzed using the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) score system. n = 5. (c) and (d) Osteophytes were semi-quantified by evaluating the osteophyte formation score consisting of two domains, size (c) and maturity (d). n = 5. (e) Quantitative micro-CT analysis of tibial subchondral trabecular bone with bone volume fraction. n = 5. (f) Quantitative micro-CT analysis of tibial subchondral bone plate thickness. n = 5. (g) Three-dimensional models of mice knee joints. Red arrow shows osteophyte formation. Scale bar, 500μm. (h) Mitochondrial morphology of mice cartilage was observed using transmission electron microscopy. Scale bar, left, 2 μm; right, 500 nm. (i-l) Quantification of mRNA levels for cartilage anabolism related genes (Col2a1, Acan, Sox9, Prg4), catabolism related genes (Mmp3, Mmp13, Adamts1, Adamts5), ferroptosis related genes (Gpx4, Acsl4, Ptgs2, Fth1) and inflammatory related genes (Ccl2, IL-6) in articular cartilage obtained from sham, vehicle, and Fer-1, DFO, Nec-1 treated mice, respectively. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, * P< 0.05; ** P< 0.01; *** P< 0.001. Student's t-test and one-way ANOVA were used for comparison between two groups and multiple groups, respectively.