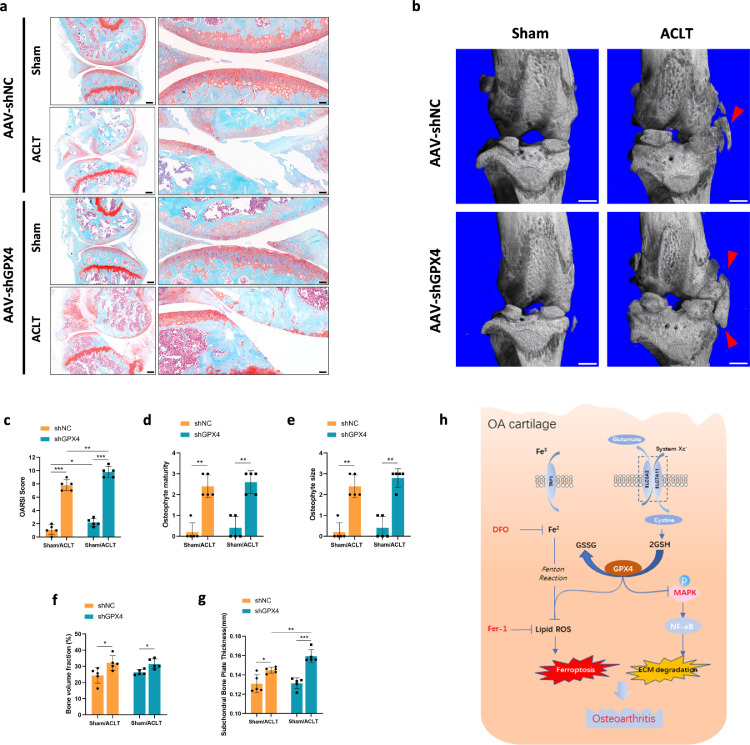
Figure 6.
GPX4 downregulation accelerated OA progression. (a) Representative safranin O-fast green images of mice knee joints. One week before surgery, C57/BL6J mice (8 weeks old) were injected intra-articularly with AAV carrying GPX4-specific shRNA and analyzed 8 weeks after surgery. Scale bar, left, 500 μm; right, 50 μm. (b) Three-dimensional models of mice knee joints. Red arrow shows osteophyte formation. Scale bar, 500μm. (c) The severity of OA-like phenotype was analyzed using the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) score system. n = 5. (d) and (e) Osteophytes were semi-quantified by evaluating the osteophyte formation score consisting of two domains, size (D) and maturity (E). n = 5. (f) Quantitative micro-CT analysis of tibial subchondral trabecular bone with bone volume fraction. n = 5. (g) Quantitative micro-CT analysis of tibial subchondral bone plate thickness. n = 5. (h) In OA cartilage, function of system Xc− was inhibited, result in content of GSH and GPX4 expression decreased. Downregulation of GPX4 not only increased the sensitivity of chondrocytes to oxidative stress, but also aggravated extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation potentially through MAPK/NFκB pathway. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, * P< 0.05; ** P< 0.01; *** P< 0.001. Student's t-test and one-way ANOVA were used for comparison between two groups and multiple groups, respectively.