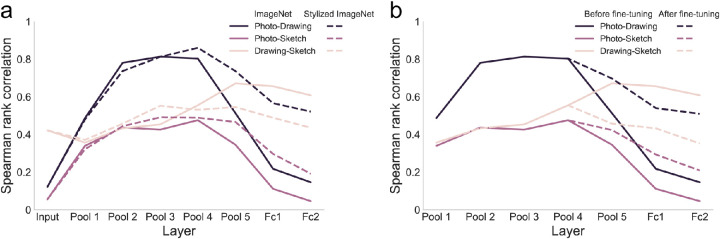
Figure 4.
Similarity in representational structure between types of depiction in variants of VGG-16. (A) Spearman rank correlations between RDMs for the different types of depiction based on the CNN input (raw pixel values of preprocessed images) as well as activations in the ImageNet-trained VGG-16 (VGG-16 IN) and activations in the VGG-16 trained on stylized ImageNet (VGG-16 SIN). Based on the CNN input, we found a low similarity between photos and both drawings and sketches. The similarity between drawings and sketches, however, was higher. After passing the images through the network, we observed a high degree of representational similarity between photos and drawings and to a lesser extent also between photos and sketches in early and intermediate layers in both networks. In the later layers, these similarities between photos and abstracted types of depiction dropped sharply in VGG-16 IN, whereas in VGG-16 SIN this drop was attenuated. (B) Spearman rank correlations between RDMs for the different types of depiction in the ImageNet-trained VGG-16 before and after fine-tuning. After fine-tuning, the similarity in the representational format was increased for the photo-to-drawing and photo-to-sketch similarity, but reduced for the drawing-to-sketch similarity, indicating increased similarity in processing between photos and abstracted types of depiction in the network after fine-tuning.