Figure 1. Comparison of Measured GFR and Estimated GFR (eGFR) According to Race Group across Alternative GFR Estimating Equations.
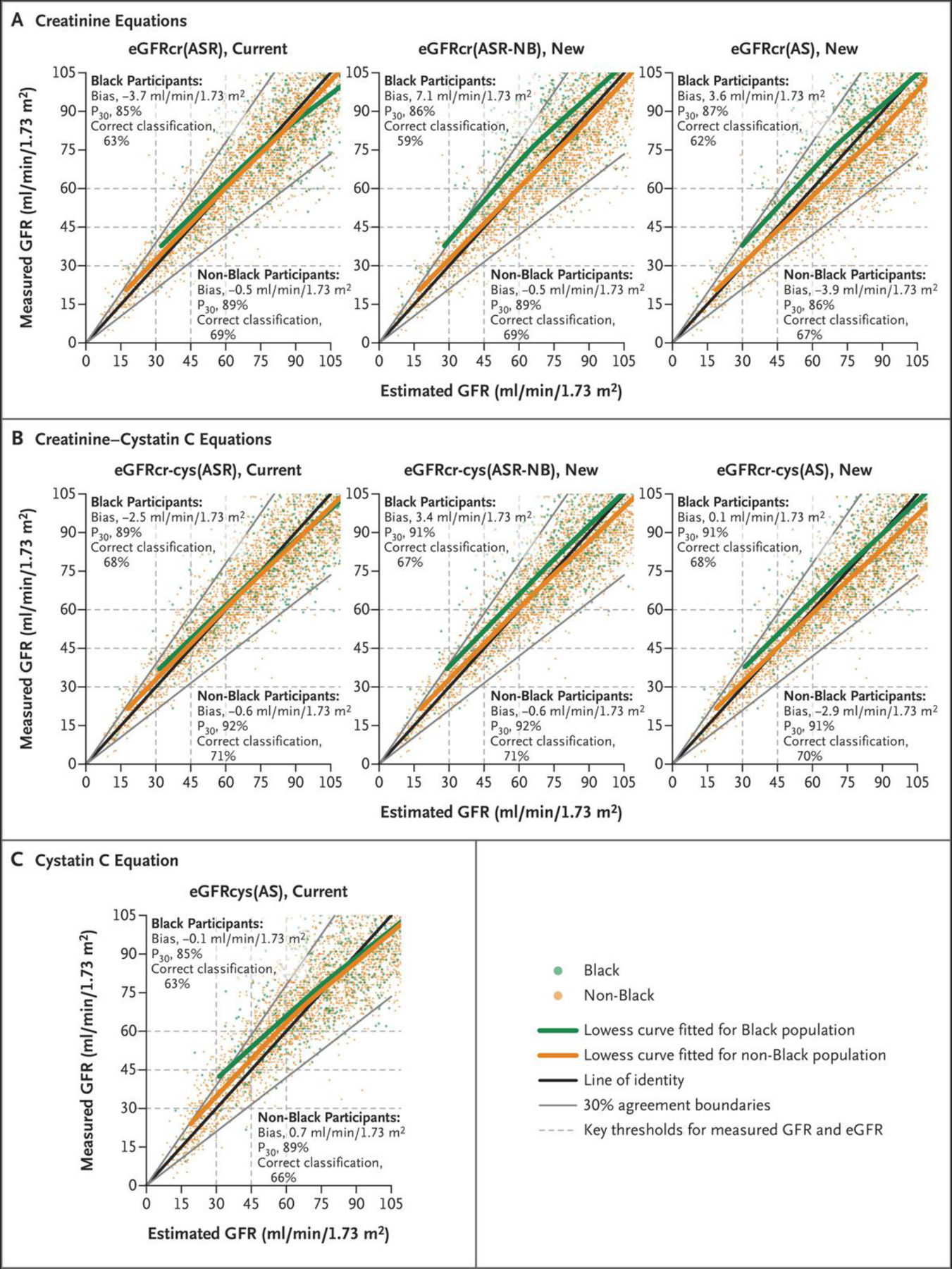
The equations are referred to by the filtration marker or markers (creatinine [eGFRcr], cystatin C [eGFRcys], or creatinine–cystatin C [eGFRcr-cys]) and the demographic factors (age, sex, and race [ASR] or age and sex [AS]) that were used in their development. Non-Black (NB) refers to equations in which the Black race coefficient was omitted in computation of the eGFR value. Data from the validation data set are shown. Data from the development data set are shown in Figure S4 in the Supplementary Appendix. Bias is defined as the median difference between measured GFR and eGFR. A positive sign indicates underestimation of measured GFR, and a negative sign indicates overestimation of measured GFR. P30 is the proportion of eGFR within 30% of measured GFR. Correct classification refers to agreement between measured GFR and eGFR categories of more than 90, 60 to 89, 45 to 59, 30 to 44, 15 to 29, and less than 15 ml per minute per 1.73 m2.
