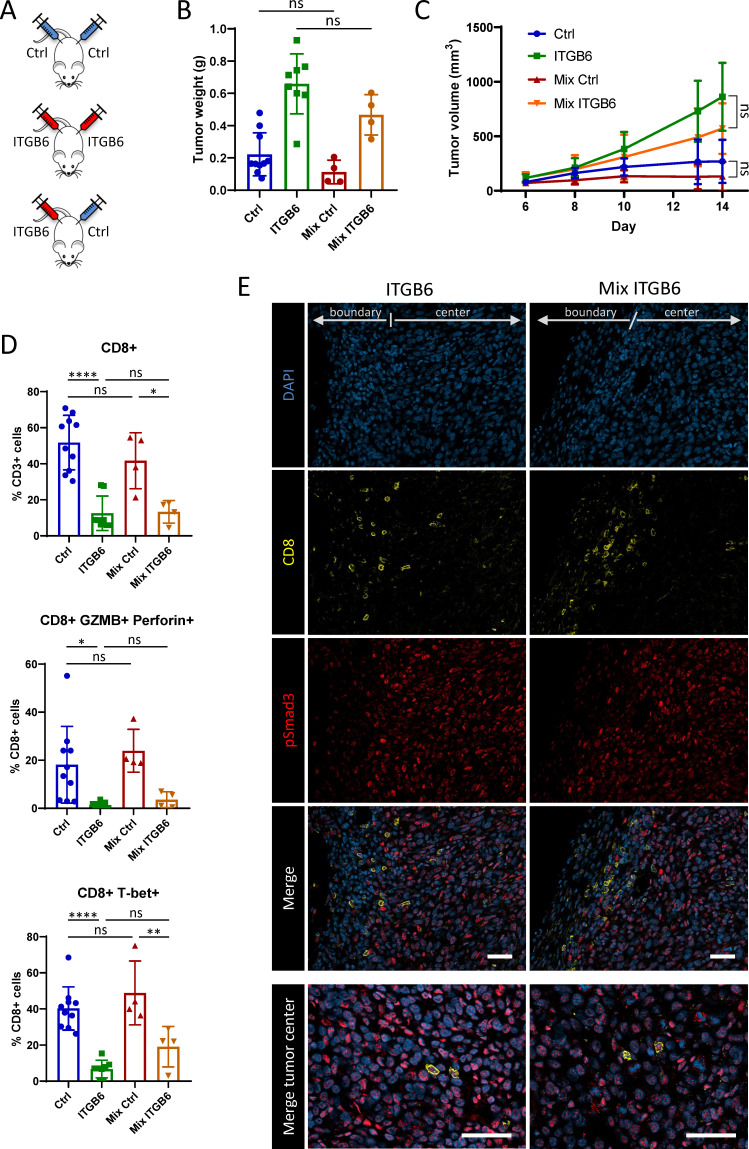
Figure 4.
ITGB6 expression leads to local, but not systemic T-cell inhibition. (A) Experimental design of injection scheme. Subcutaneous injection of CT26-Ctrl tumors or CT26-ITGB6 tumors in both flanks or CT26-Ctrl tumors in one flank and CT26-ITGB6 tumors in the other flank of the mice (Mix). (B) Weight of tumors from mice bearing only CT26-ITGB6 or CT26-Ctrl tumors or mice bearing both tumors (Mix). (C) Tumor volume development of tumors from mice bearing only CT26-ITGB6 or CT26-Ctrl tumors or mice bearing both tumors (Mix). (D) Flow cytometry analysis of T-cells isolated from tumors of mice bearing only CT26-ITGB6 or CT26-Ctrl tumors or mice bearing both tumors (Mix). (E) Immunofluorescent stainings for CD8 and pSmad3 in CT26-ITGB6 tumors from mice bearing only CT26-ITGB6 tumors or mice bearing both tumors (Mix). Means and SDs are shown (n=5 mice). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (B and D) and two-way ANOVA (C) with Tukey’s post-hoc test were used to calculate statistical significance. ns=not significant (p≥0.05), *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.