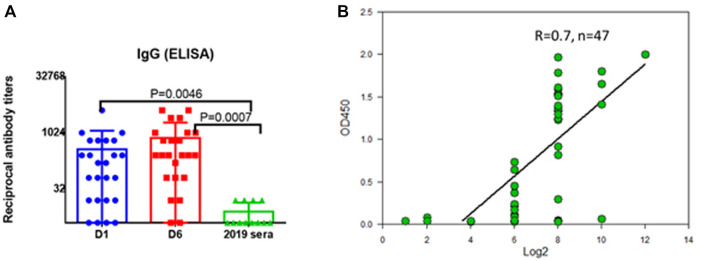
FIGURE 2.
Serum IgG to recombinant SarsS-protein in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. (A) D1—first day of hospital stay (n = 28), D6—sixth day of hospital stay (n = 28), 2019 sera were obtained from the patients examined in 2019 (n = 14). (B) 47 serum samples from patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were studied using a commercial kit for detecting IgG antibodies to coronavirus “SARS-Cov-2 IgG Screen” (Imbian, Russia) in comparison with recombinant S1 protein. A high level of correlation was shown (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient = 0.7, n = 47) when detecting serum antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 using a recombinant protein and using a commercial kit. A high level of correlation was shown when serum IgG were detected using “SARS-Cov-2 IgG Screen” kit or recombinant S-protein, Spearmen r = 0.7. The positive value according to the screen data corresponded to 1:256 antibody titers obtained using S-protein.