FIGURE 2.
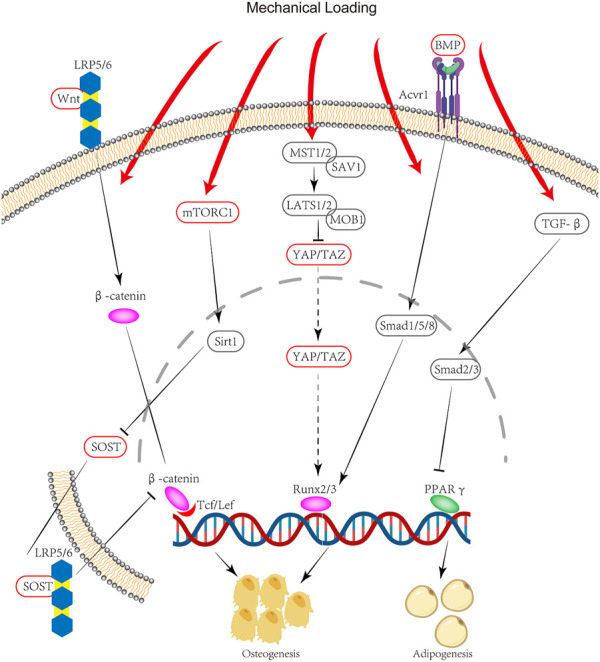
Signaling pathway of HO due to mechanical stimulation: Mechanical stimulation through mTORC1 leads to an increase in Sirt1 translocation into the nucleus, followed by a decrease in SOST secretion. SOST can bind to LRP5/6 to inhibit β-catenin. Mechanical loading can also activate Runx2/3 gene expression through YAP/TAZ. Thus mechanical stimulation promotes osteogenic gene expression through mTORC1 and YAP/TAZ. Meanwhile, mechanical stimulation can inhibit PPARγ gene expression through the TGF-β pathway, thereby suppressing lipogenic differentiation. These combined effects lead to a stem cell fate shift.
