Figure 3.
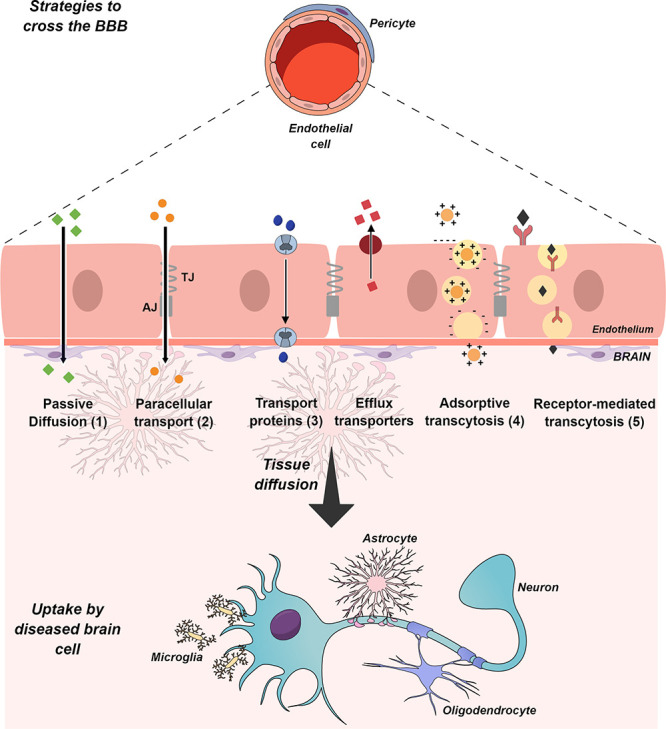
Schematic representation of the blood–brain barrier and the main transport routes for permeation and transport across the endothelium. (1) Small lipid-soluble agents can passively diffuse through the lipid bilayer. (2) Only small water-soluble molecules can diffuse through the intercellular spaces between endothelial cells. (3) The endothelium contains carriers for glucose, amino acids, nucleosides, purine bases, choline, and other substances. (4) Cationic molecules such as albumin and other plasma proteins are taken up by adsorptive-mediated transcytosis, which is consecutive of the endocytosis/exocytosis event. (5) Ligands such as insulin, transferrin, cholesterol-containing particles, and most other protein hormones are taken up by specific receptor-mediated transcytosis. Once across the BBB, the compounds must diffuse toward the disease site and be taken up by the diseased cells. TJ, tight junction; AJ, adherens junction.
