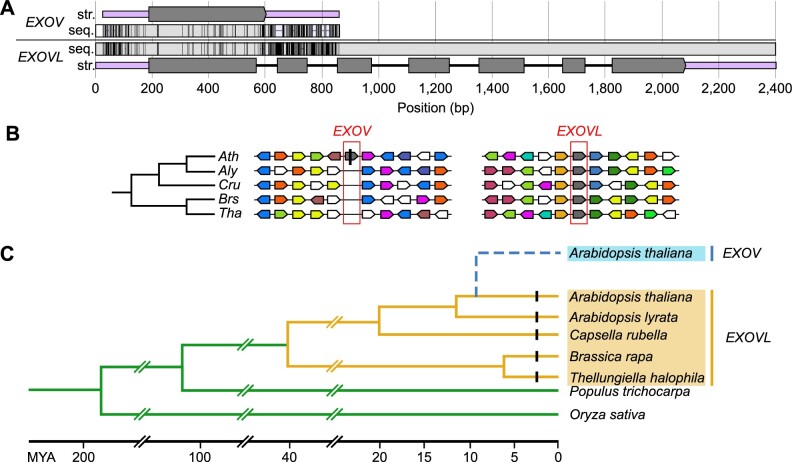
Figure 1.
Evolution of EXOV (At3g57110), a partial gene duplication from EXOVL (At5g60370), as inferred from gene structure and syntenic analysis. A, Complete alignment of the sequence (seq.) and gene structure (str.) of the new gene EXOV (At3g57110) and the parental gene EXOVL (At5g60370). Gray boxes, exons; black line, introns; light purple box, untranslated regions (UTRs); black vertical lines in EXOV and EXOVL indicate unmatched nucleotides. B, Syntenic analysis of the new gene EXOV and the parental gene EXOVL based on the phylogenic tree. Ath, Arabidopsis thaliana; Aly, Arabidopsis lyrata; Cru, Capsella rubella; Bra, Brassica rapa; Tha, Thellungiella halophila. The red blocks highlight the orthologous regions of EXOV and EXOVL in the other four related species, showing no orthologous copies for EXOV and four orthologous copies for Aly (Aly496275), Cru (Carubv10026530m), Bra (Bra020254), and Tha (Thhalv10013696). Inspection of 10 genes that flank EXOV (the gray arrow block with vertical bar) and EXOVL (the gray arrow block) indicates orthologous syntenic arrangement of these genes in support of the orthologous comparison in the highlighted genomic regions of EXOV and EXOVL in the A. thaliana relatives. The arrows show the orientation of the genes. The colors represent homologous relationships and a color represents a distinct homologous gene. C, Phylogeny and divergence time between A. thaliana and its relatives and the species distribution of the new gene EXOV and the parental gene EXOVL.