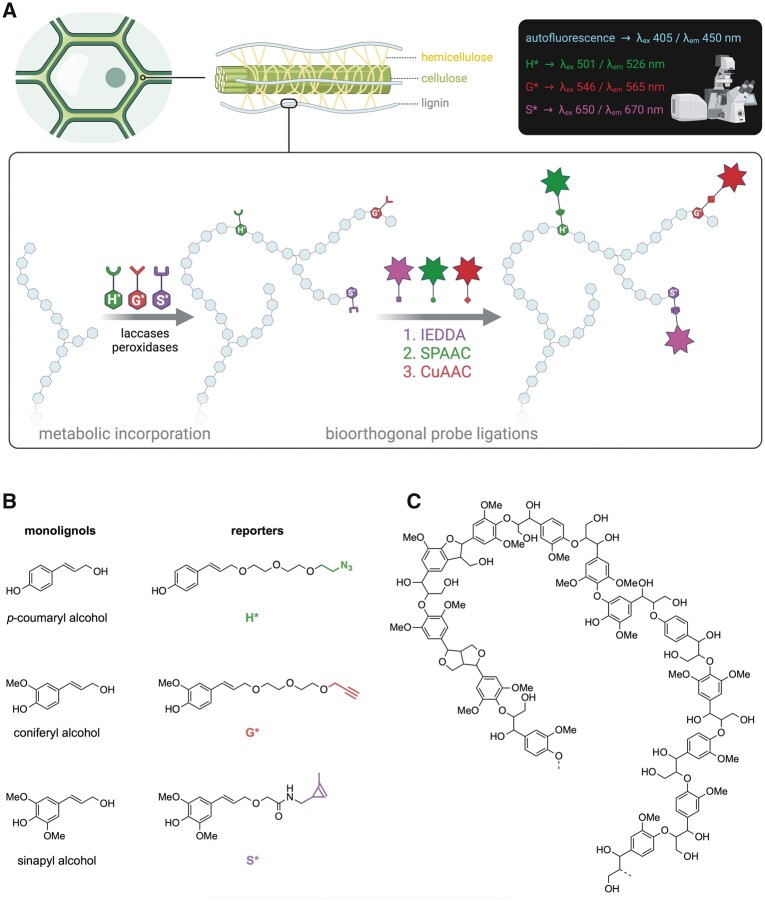
Figure 2.
Lignin bioorthogonal triple labeling and chemical reporter structure. A, Schematic representation of the lignin bioorthogonal triple labeling strategy in plant cell walls. Monolignol chemical reporters H*, G*, and S* are oxidized by cell wall located PRXs and/or laccases and become metabolically incorporated into the growing lignin polymer. Following reporter incorporation, green, red, and magenta fluorescent probes are added and become specifically linked to H*, G*, and S* reporters, respectively, via three sequential bioorthogonal reactions: IEDDA (S*), SPAAC (H*), and CuAAC (G*). Spatial localization of fluorophores is analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). B, Chemical structures of native lignin monolignols (left) and corresponding chemical reporters H*, G*, and S* (right). Reporter tags involved in the bioorthogonal reaction with the corresponding fluorophores are shown in color: green—azide group, red—alkyne group, magenta—methyl cyclopropene group. C, Example of typical lignin oligomer structure.