Figure 7.
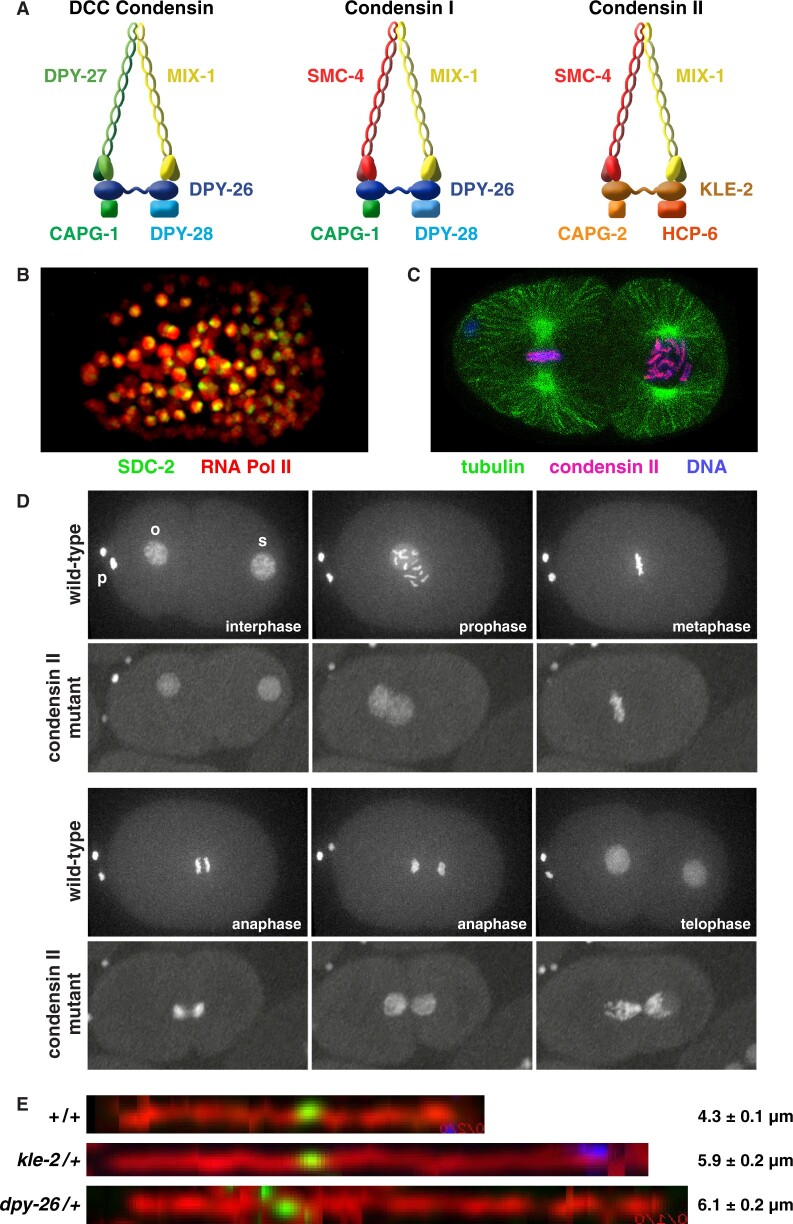
Three condensin complexes carry out distinct functions in C. elegans. (A) Comparison of the DCC condensin complex compared with the two other independent condensin complexes in C. elegans. The DCC condensin binds to X chromosomes and reduces X expression in XX embryos (B). It shares four subunits with condensin I as shown; DPY-27 replaces SMC-2 as the fifth subunit. Condensin I plays minor roles in chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis. Condensin II is the prime condensin complex responsible for mitotic and meiotic chromosome compaction, resolution, and segregation. It shares one subunit with the DCC (MIX-1) and two subunits (SMC-4 and MIX) with condensin I. (B) SDC-2 is bound to both X chromosomes. Shown is an XX embryo expressing SDC-2::mNeonGreen (green) and RNA Polymerase II::mRuby (red), which is dispersed throughout the nucleus. (C) Condensin II binding on holocentric mitotic chromosomes. Shown is a two-cell embryo with one cell in metaphase (left) and one in prophase (right). Condensin II (magenta) colocalizes with holocentric chromosome binding proteins all along the outer edge of each chromosome (blue), adjacent to where the mitotic spindle (green) attaches. (D) Disruption of condensin II causes severe defects in mitotic chromosome segregation. Shown is a progression of images, from fertilization through the first cell division, of a single wild-type or hcp-6 mutant embryo carrying GFP::H2B histone-tagged chromosomes. In hcp-6 mutants, prophase chromosomes are not properly condensed, chromosomes fail to align properly on the metaphase plate, and chromatin bridges occur between separating homologous chromosomes in anaphase, thereby preventing chromosome segregation, as seen by the fully connected sperm and oocyte chromosomes in telophase. o, oocyte pronucleus; s, sperm pronucleus; p, polar bodies. (E) Axis lengths of meiotic pachytene chromosomes are extended in mutants depleted of condensin I or condensin II. Shown are images of computationally straightened X-chromosome axes in pachytene nuclei of wild-type animals or heterozygous condensin mutants that were labeled for the cohesin axis protein COH-3/4 (red), a center X FISH probe (green), and a right end X FISH probe (blue). Chromosomes are displayed horizontally. Genotypes of animals and average total chromosome axis length with SEM are shown adjacent to each image.