Figure 1.
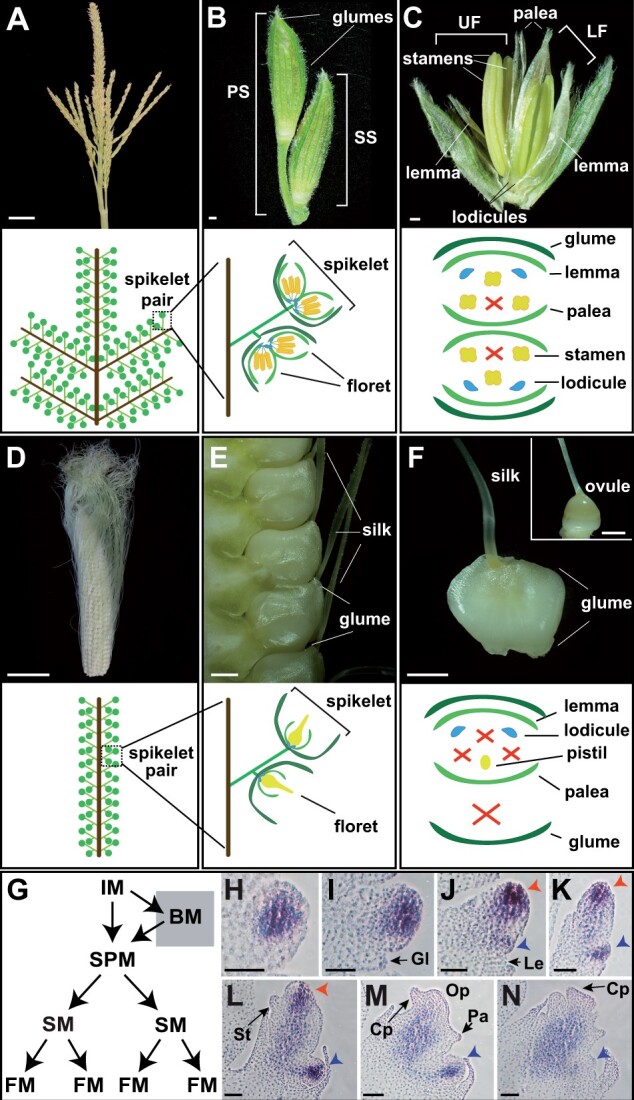
Normal maize floral development. A, Mature tassel, the male inflorescence. B, Pair of tassel spikelets. C, Dissected tassel spikelet, exposing two male florets. D, Mature ear, the female inflorescence. E, Mature ear spikelets. F, Dissected ear spikelet, containing a single female floret. Inset is a mature ovule with glumes and other floral organs removed. G, Diagram depicting meristems in the inflorescence. H–N, RNA in situ hybridization of the meristem marker, kn1, in developing ear spikelets; Red and blue arrowheads indicate upper and lower FM, respectively. PS, pedicellate spikelet; SS, sessile spikelet; UF, upper floret; LF, lower floret; IM, inflorescence meristem; BM, branch meristem; SPM, spikelet pair meristem; SM, spikelet meristem; Gl, glume; Op, ovule primordia; Cp, carpel primordia; Lo, lodicule; St, stamen; Le, lemma; Pa, palea. Scale bars: (A and D) = 5 cm, (B, C, E, and F) = 500 μm, (H–N) = 50 μm.
