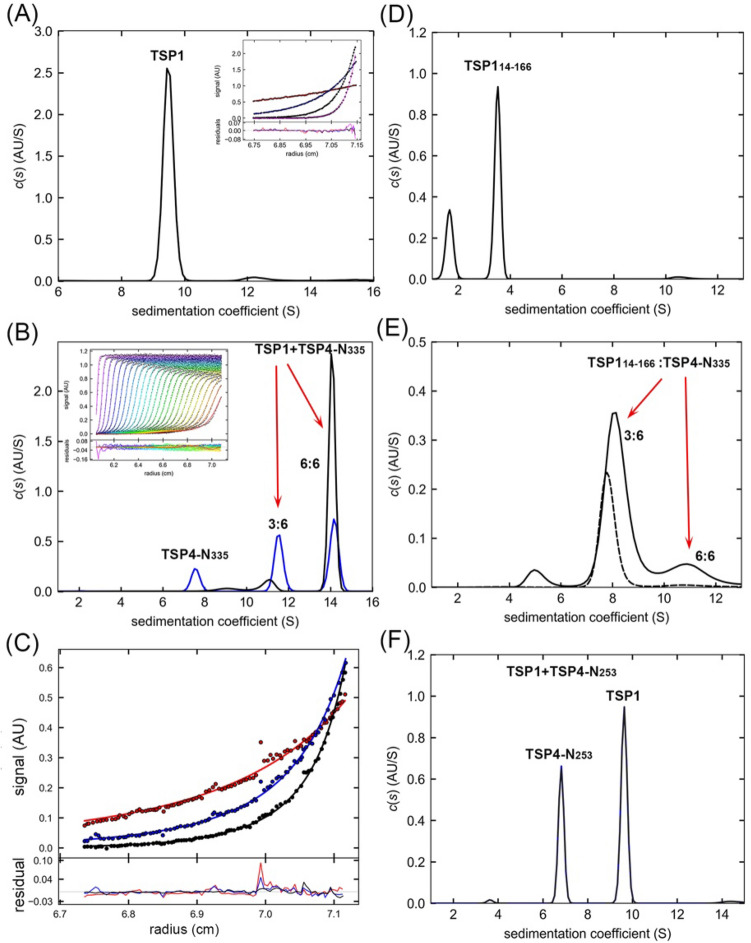
Figure 6.
AUC analyses of TSP1 and its association with TSP4-N proteins. (A) The c(s) distribution of 8.1 μM TSP1. Insert: SE profile of 3 μM TSP1 with a best fit RMSD of 0.012 AU, collected at 3, 6, 8 and 12 krpm rotor speeds. The best fits are shown as black solid lines through the experimental data with MWapp of 226 kDa. (B) The c(s) distribution profiles of 3.6 μM TSP4-N335 hexamer with 2.8 μM TSP1 (blue) and with 6.4 μM TSP1 (black). Insert: Direct Lamm-Equation modeling of the SV experiment containing 3.6 μM TSP4-N335 and 6.4 μM TSP1. The best fits are shown as solid lines through the experimental data. (C) SE profile of 1.0 μM each of TSP4-N335 and TSP1 with a best fit RMSD of 0.011 AU, collected at 4, 6 and 8 krpm rotor speeds. The best fits are shown as solid lines through the experimental data with Kd = 0.08 μM. The LEq analysis of SV data and that of SE profiles were calculated with global best-fit distributions using a [A + B + B ↔ AB + B ↔ ABB] model with 2 symmetric sites and macroscopic association constant KA. The combined residuals in AU from the same cell at different rotor speeds are shown below the plot. (D) The c(s) distribution profiles of 3.3 μM TSP114-166, missing the N-terminal 14 amino acids, in the presence of 100 μM ZnCl2. (E) The c(s) distribution profiles of a mixture of 3.3 μM TSP4-N335 (dashed line) and of a mixture of 3.3 μM TSP4-N335 and 13 μM TSP1-N14-166 (solid line). (F) The c(s) distribution profiles of a mixture of 5.4 µM TSP4-N253 and 3.3 µM TSP1.