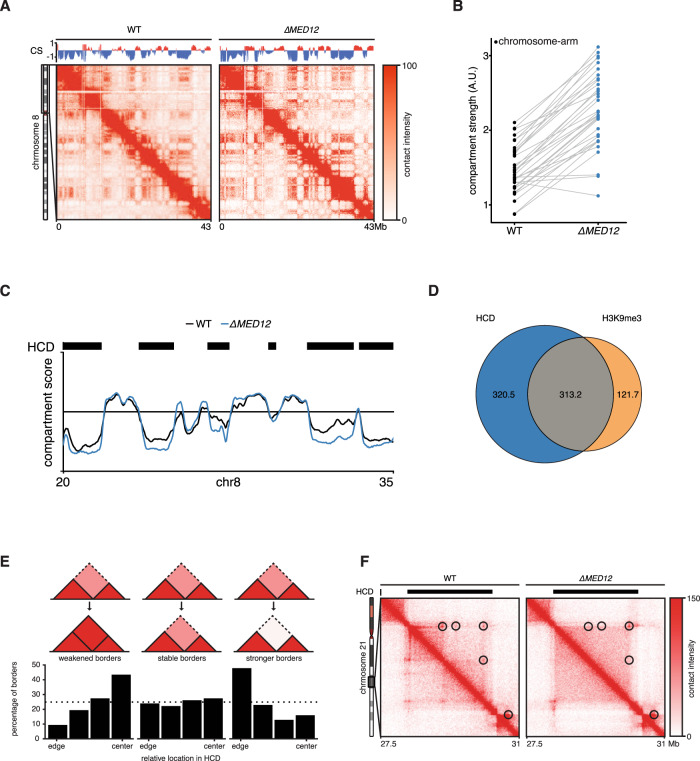
Fig. 3. Loss of MED12 affects 3D genome organization.
A ICE normalized Hi-C contact matrices at 100 kb resolution for WT and ∆MED12 are shown for the p arm of chromosome 8. Above the matrices the compartment score is plotted. Contact matrices are visualized using GENOVA. B The compartment strength is calculated for all chromosome arms in WT and ∆MED12 cells. Lines connect scores for the same chromosome arm. C Compartment scores for a specific region on chromosome 8 for WT (black) and mutant (blue) cells. Black rectangles show hypercompartmentalized domains (HCDs) identified by a custom hidden markov model. D Venn diagram shows the overlap in genome-wide coverage between HCDs identified in ∆MED12 and H3K9me3 domains identified in WT cells. E TAD borders in HCDs were stratified into three categories depending on their difference in TAD separation (“weaker”, “unchanged”, “stronger”). The relative position within an HCD is plotted. F ICE normalized Hi-C contact matrix at 20 kb resolution for WT and ∆MED12 cells are shown for a region on chromosome 21. Contact matrices are visualized using GENOVA. Black rectangles indicate the position of HCD.