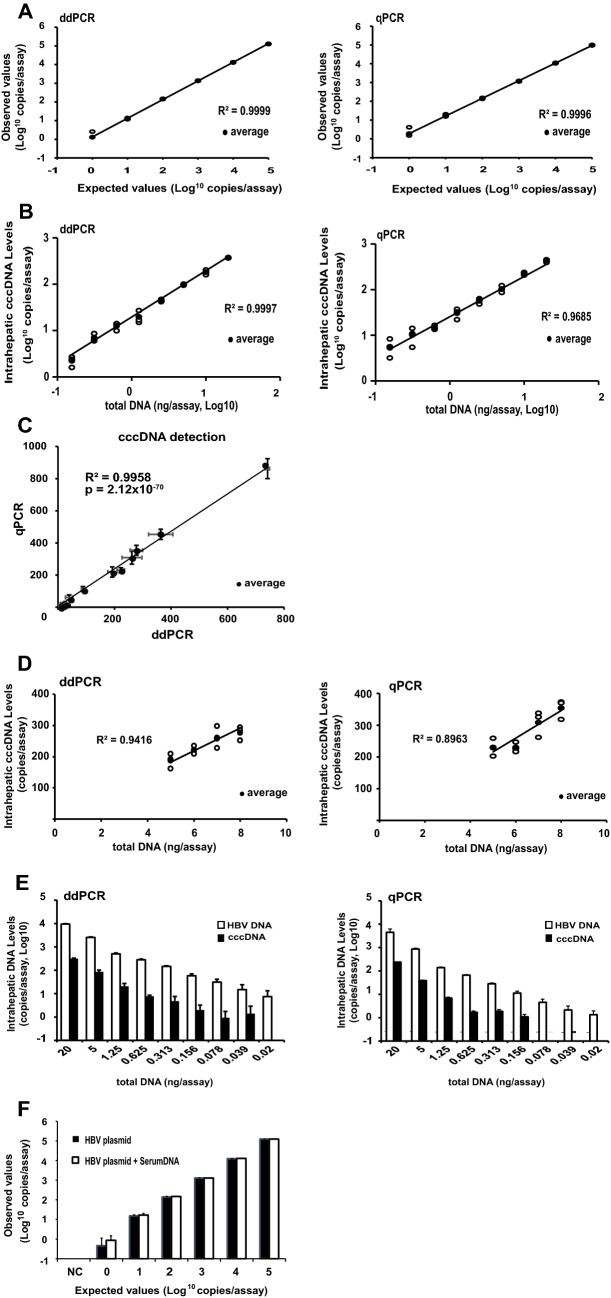
Figure 2.
Comparison of ddPCR to real-time PCR for quantitation of cccDNA. (A) The plasmid containing the HBV genotype C2/Ce DNA genome (AB246345) was measured using a tenfold dilution of DNA ranging from 105 to 100 copies/assay by ddPCR or real-time PCR. (B) Intrahepatic cccDNA levels in the liver of chimeric mouse infected with HBV were measured using various amounts of DNA ranging from 20 to 0.156 ng/assay by ddPCR or real-time PCR. (C) The intrahepatic cccDNA levels measured by ddPCR and real-time PCR revealed substantial agreement. (D) Intrahepatic cccDNA levels from the liver of chimeric mouse with HBV infection were measured using various amounts of DNA, ranging from 8 to 5 ng/assay. (E) Intrahepatic HBV DNA and cccDNA levels in the liver of chimeric mouse infected with HBV were measured using various amounts of DNA ranging from 20 to 0.02 ng/assay by ddPCR or real-time PCR. Each assay was conducted in triplicate. Target concentrations were repeatedly and independently tested three times. (F) The comparison of the HBV plasmid using a tenfold dilution of DNA ranging from 105 to 100 copies/assay with or without the sera from IC patient (#9 in Fig. S3C) by ddPCR. The cccDNA signal in the absence of the HBV plasmid was negative irrespective of the sera.