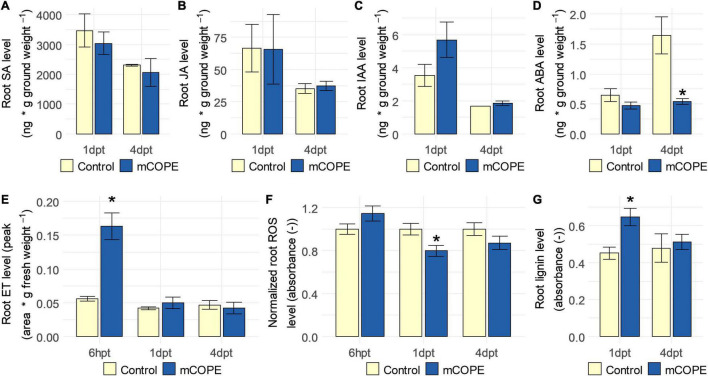
FIGURE 4.
Establishment of induced resistance (IR) via Cucurbitaceae COld Peeling Extract (CCOPE) derived from melon (Cucumis melo var. cantalupensis; mCOPE) is associated with ethylene (ET) accumulation, lowered abscisic acid (ABA) concentrations, decreased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a transient increase in lignin content in roots of rice plants. Shoots of 14-days-old rice plants were treated with the buffer used for CCOPE preparation (Control) or mCOPE. Six hours, 1 day and/or 4 days later (6 hpt, 1 dpt, and 4 dpt, respectively), roots were collected to quantify levels of (A) salicylic acid (SA), (B) jasmonic acid (JA), (C) indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), (D) ABA, (E) ET, (F) ROS, and/or (G) lignin. (A–G) Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate significant differences upon comparison of mCOPE-treated plants with same-aged, mock-treated control plants. Statistical differences were determined via a two-sided heteroscedastic t-test (p < 0.05). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences upon comparison of CCOPE- and mock-treated cells.