Figure 2. Metabolism of γT -.
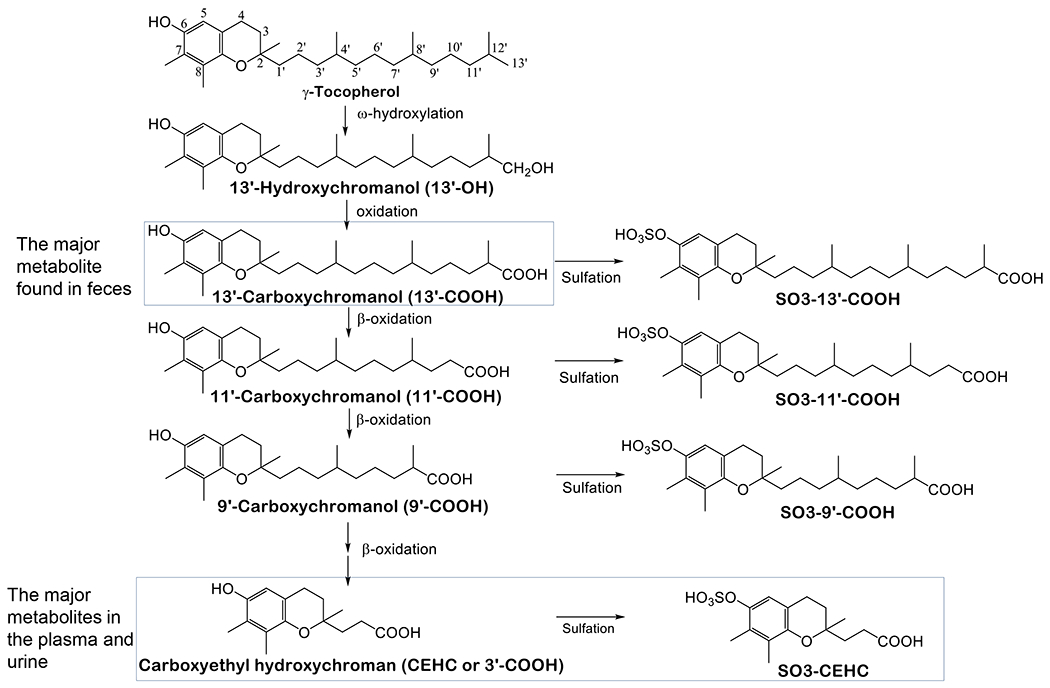
γT is metabolized by CYP4F2-catalyzed ω-hydroxylation and ω-oxidation to form 13’-OH and 13’-COOH. 13’-COOH is further metabolized via β-oxidation to generate shorter-chain carboxychromanols and terminal metabolite, γ-CEHC. Studies in animal and humans show that 13’-COOH appears to be the most abundant metabolite found in feces, and γ-CEHC and conjugated γ-CEHC are the major metabolites in the blood and urine.
