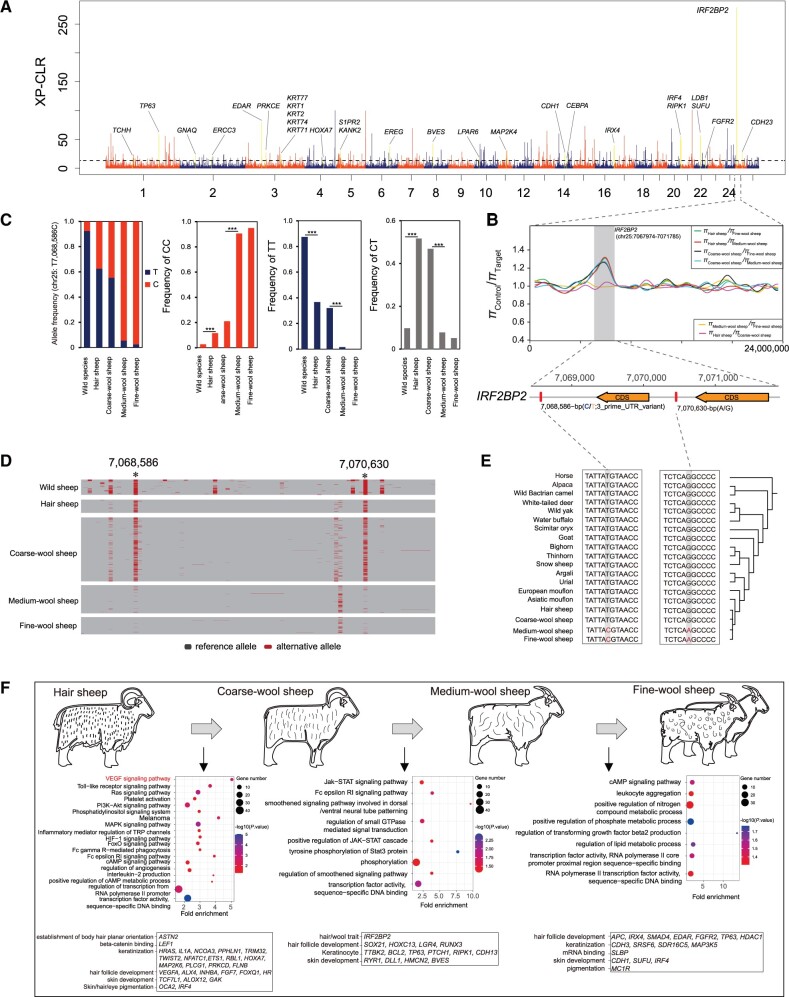
Fig. 7.
Genomic evolution of hair/coarse-wool/medium-wool/fine-wool sheep. (A) Whole-genome selective signals between fine-wool and hairy populations of domestic sheep by the cross-population composite likelihood ratio (XP-CLR) test. (B) Six comparisons of π ratio (πHair sheep/πCoarse-wool sheep, πHair sheep/πMedium-wool sheep, πHair sheep/πFine-wool sheep, πCoarse-wool sheep/πMedium-wool sheep, πCoarse-wool sheep/πFine-wool sheep and πMedium-wool sheep/πFine-wool sheep) indicates strong selective signal in IRF2BP2 gene. (C) Allele frequency of the mutation site and frequencies of genotypes CC, TT, and CT in 3′-UTR of IRF2BP2 (chr25: T7,068,586C), and significance of the genotype difference is tested. (D) Haplotype pattern of IRF2BP2 among wild sheep, hairy, coarse-wool, medium-wool, and fine-wool populations of domestic sheep. (E) Sequence comparison among different species at mutations chr25: 7,068,586, and chr25: 7,070,630. (F) GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses, with the significant (P < 0.05) GO terms and pathways and associated genes shown.