FIG 1.
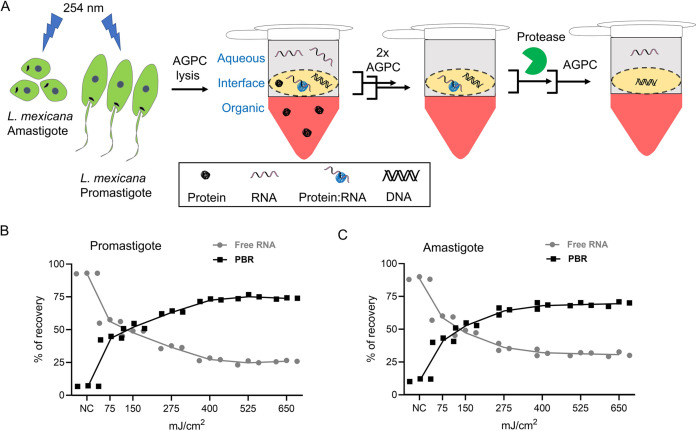
OOPS recovers protein-bound RNAs (PBRs) in Leishmania. (A) Schematic representation of the OOPS method to extract PBRs in L. mexicana promastigotes and axenic amastigotes. UV-irradiation of the live Leishmania parasites induce RNA-protein cross-linking. Upon cell lysis and AGPC phase-partitioning, the protein-RNA adducts, which have physical properties of both proteins and RNAs, are simultaneously drawn to the organic and aqueous phases and therefore accumulate in the interface. Sequential AGPC phase-partitioning followed by protease digestion of the interface and a final AGPC separation yields the previously PBRs in the aqueous phase. Relative proportions of free-RNAs (aqueous phase) and PBRs (interface) with increasing UV-dosage in promastigotes (B) and in axenic amastigotes (C). The free RNA and PBR were quantified using QuantiFluor RNA system (Promega). The sum of the free RNA and PBR provided the total absolute quantities of RNA recovered at each UV-dosage. Percentage of recovery of free RNA and PBR was calculated based on the total RNA recovered. Data shown as mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. NC: non-cross-linked controls.