FIG 2.
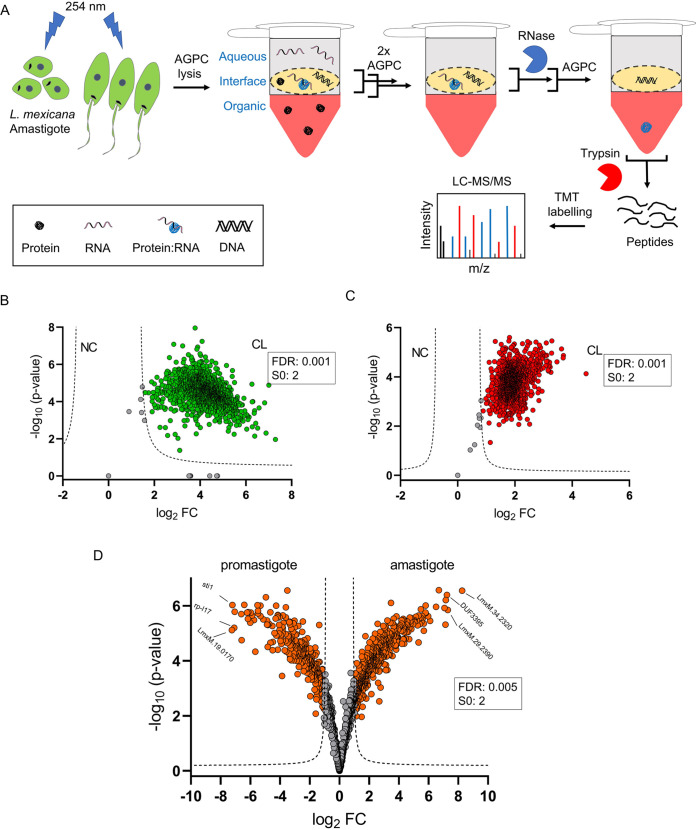
OOPS recovers RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) in Leishmania. (A) Schematic representation of combination of OOPS with TMT-labeling and LC-MS/MS that enables discovery and quantitation of RBPs in L. mexicana promastigotes and axenic amastigotes. Following UV cross-linking, cell lysis and three rounds of AGPC phase-partitioning, the third interface that is enriched with the protein-RNA adducts is collected and treated with RNase. A final AGPC phase-partitioning of the RNase-treated interface yields the previously RNA-bound proteins in the organic phase. The RBPs precipitated from the organic phase are subjected to tryptic digestion and isobaric labeling using tandem mass tags (TMT). LC-MS/MS analysis of the TMT-labeled samples provide identification of the RBPs and their fold change (FC) in the cross-linked (CL) samples compared to non-cross-linked (NC) controls. All experiments were performed in three biological replicates. Scatterplot showing CL-specific enrichment of RBPs in the OOPS interface of L. mexicana promastigotes (B) and axenic amastigotes (C). A modified t test with permutation-based FDR statistics (250 permutations, FDR = 0.001) was applied to compare three replicates of CL and NC samples in each life cycle stages. (D) Volcano plot showing differential enrichment of RBPs in the promastigote and axenic amastigote life cycle stages of L. mexicana. A modified t test with permutation-based FDR statistics (250 permutations, FDR = 0.005) was applied to compare the promastigote and amastigote groups.