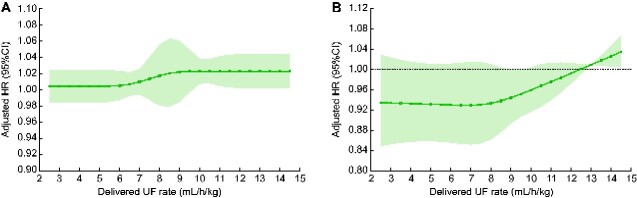
FIGURE 3.
Adjusted associations between mean delivered UF rate and incident atrial fibrillation when UF rate is modeled as a cubic spline (per 1 mL/h/kg). The solid black lines indicate multivariable-adjusted HRs for incident atrial fibrillation as a function of UF rate and the light gray shading represents the associated 95% CIs. (A) Adjusted HRs and 95% CIs comparing UF rate values 1 mL/h/kg apart where the comparator is lower. (B) Adjusted HRs and 95% CIs comparing UF rate values to a reference of 13 mL/h/kg. All models are adjusted for year of incident dialysis-dependent kidney failure, age, sex, race, Hispanic ethnicity, census division, socioeconomic status variables, Medicare/Medicaid dual eligibility, comorbid conditions (Table 1), number of hospital days in 30 days prior to UF rate ascertainment period, vascular access type, predialysis systolic and diastolic BP, number of hemodialysis treatments in the UF rate ascertainment period and serum albumin, eGFR, potassium and calcium. Estimates are presented for UF rates between 2.5 and 14.5 mL/h/kg (the 5th and 95th percentiles of delivered UF rate in the study sample, respectively). AFib, atrial fibrillation; UF rate, mean delivered UF rate (mL/h/kg).