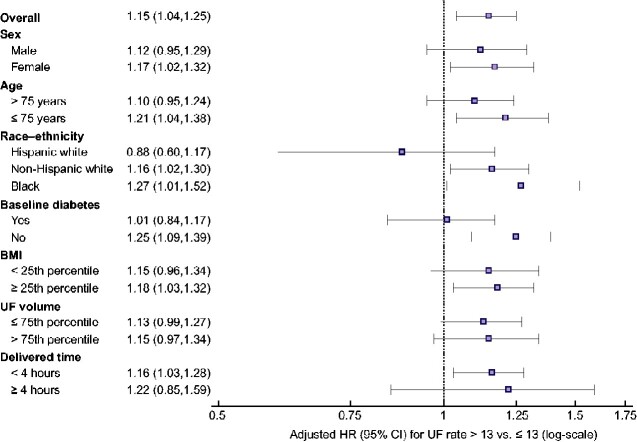
FIGURE 4.
Association between UF rate >13 (versus ≤13) mL/h/kg and incident atrial fibrillation within clinically relevant subgroups. Extended Cox models with multiple imputation for missing data were used to compute adjusted HRs and 95% CIs for the association of delivered UF rate exposure (<13 versus ≥13 mL/h/kg) and incident atrial fibrillation. All models were stratified by year of incident end-stage kidney disease. Models were adjusted for age, sex, race, Hispanic ethnicity, census division, socioeconomic status variables, Medicare/Medicaid dual eligibility, all comorbid conditions listed in Table 1, number of hospital days in the 30 days prior to the UF rate ascertainment period, vascular access type, predialysis systolic and diastolic BP, number of dialysis treatments during the UF rate ascertainment period and serum albumin, eGFR, potassium and calcium. The subgroups of body mass index, UF volume and delivered treatment time were restricted to the 14 695 patients without missing UF rate–related data in the follow-up time period. UF rate, mean delivered UF rate (mL/h/kg).