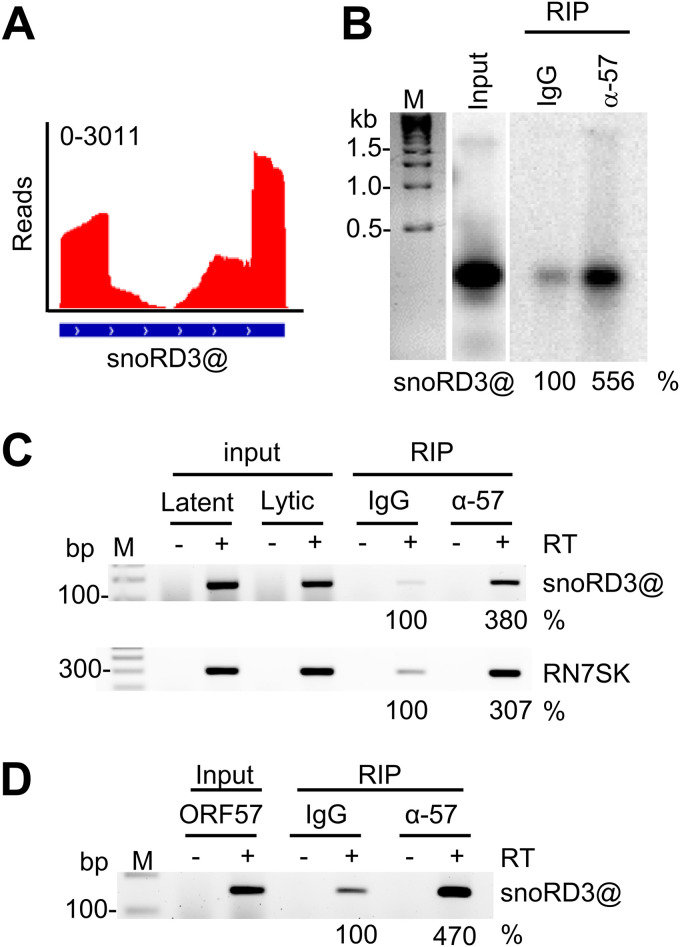
FIG 6.
ORF57 binds the snoRD3@ with unknown RNA targets. (A and B) Distribution of ORF57 CLIP-seq reads mapped to snoRD3@ (A) and Northern blot verification of snoRD3@ interaction with ORF57 in BCBL-1 cells by anti-ORF57 antibody RIP and then by 32P-labeled antisense DNA oligonucleotide probe oBAH135, specific to all members of snoRD3@ (B). IgG served as a RIP control. (C) RT-PCR of ORF57 immunoprecipitated RNAs from BCBL-1 cells with VA-induced KSHV lytic infection in the absence or presence of reverse transcriptase. IgG served as a negative RIP control. Total RNA extracted from the cells with latent or lytic KSHV infection was examined for relative levels of snoRD3@ and RN7SK RNAs, and the RNA from the cells with KSHV lytic infection also served as a lytic RNA input control. (D) RT-PCR in the absence or presence of reverse transcriptase using ORF57 immunoprecipitated RNAs from HEK293T cells with ectopic ORF57 expression. IgG served as a negative RIP control. Total RNA from HEK293T cells 24 h after ORF57 plasmid transfection was used as an input control. The following primer pairs were used: oBAH198 and oBAH199 for detection of snoRD3@ and oBAH192 and oBAH193 for detection of RN7SK. Northern blot or RT-PCR band intensity representing the immunoprecipitated RNA was calculated after normalized to the corresponding input, with IgG control as 100%.