FIG 7.
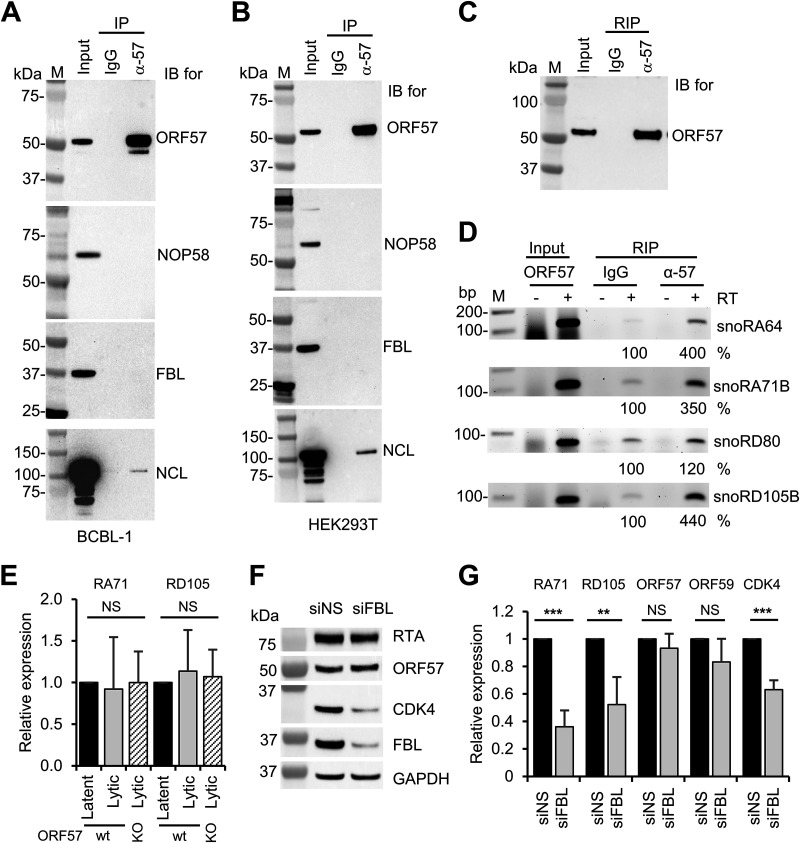
Relationship of ORF57 in snoRNA binding and expression with snoRNA-binding proteins fibrillarin and NOP58. (A) ORF57 does not interact with fibrillarin or NOP58 in BCBL-1 cells with KSHV lytic infection. Total cell extract from BCBL-1 cells under viral lytic infection was immunoprecipitated with an anti-ORF57 antibody, and the ORF57 complexes in the IP pulldowns were resolved by SDS-PAGE for detection of ORF57, fibrillarin (FBL), and NOP58 by Western blotting with the corresponding antibodies. Nucleolin (NCL) served as a positive control of cointeraction with ORF57. (B) Total cell extract from HEK293T cells transfected with an ORF57 expressing vector (pVM7) was also used for the co-IP and Western blotting as performed for panel A. (C and D) Ectopic ORF57 in HEK293T cells interacts with selective snoRNAs. (C) Representative Western blot of immunoprecipitated ORF57 from HEK293T cells expressing ORF57 by mouse monoclonal anti-ORF57 antibody. (D) RT-PCR for detection of snoRA64, snoRA71B, snoRD80, and snoRD105B in the absence or presence of reverse transcriptase (RT) using ORF57 immunoprecipitated RNAs from HEK293T cells with ectopic ORF57 expression for 24 h. IgG served as a negative RIP control. Total RNA from HEK293T cells expressing ORF57 served as an input control. See Table 1 for primer pair details for individual snoRNA detection. RT-PCR band intensity representing the immunoprecipitated RNA was calculated after normalization to the corresponding input, with IgG control as 100%. (E) ORF57 expression in iSLK/Bac16 cells does not affect the expression of snoRA71B (RA71) or snoRD105B (RD105). Total RNA isolated from iSLK/Bac16 cells bearing a wild-type KSHV genome or an ORF57-null genome (ORF57 knockout [KO]) (11) in viral latent or lytic infection induced by Dox and sodium butyrate for 48 h was used for RT-qPCR to detect the expression of representative snoRA71B and snoRD105B. GAPDH RNA served as an internal control to normalize the quantification of each snoRNA level. (F and G) Knockdown of fibrillarin expression in iSLK/Bac16 cells carrying a wt KSHV genome led to reduce the expression of snoRA71B and snoRD105B and CDK4 but not the expression of viral ORF57, ORF59, or RTA. The iSLK/Bac16 cells were first treated with a siRNA specific for fibrillarin (siFBL) or a nontargeting control siRNA (siNS) for 36 h and then induced for lytic KSHV infection for 12 h by Dox and sodium butyrate treatment before total RNA and protein extraction. Total protein lysates were blotted for viral RTA and ORF57 and host CDK4, FBL, and GAPDH by the individual corresponding antibodies. GAPDH protein served as a sample loading control (F). Total cell RNA was examined by RT-qPCR for the expression of snoRA71B, snoRD105B, viral ORF57 and ORF59, and host CDK4 (G). The bar graphs in panels E and G show means ± SD from three separate experiments, with latent RNA (E) and siNS RNA (G) as 1. Statistical analysis for RT-qPCR in panels E and G was performed by two-tailed Student’s t test. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. NS, no significance.